Overexpression of mitochondrial antioxidant manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) provides protection against AZT- or 3TC-induced endothelial dysfunction
- PMID: 25260898
- PMCID: PMC4415438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.09.010
Overexpression of mitochondrial antioxidant manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) provides protection against AZT- or 3TC-induced endothelial dysfunction
Abstract
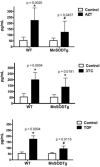
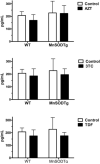
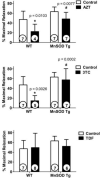
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) are considered the backbone of current combination therapies for HIV. These therapies have significantly decreased mortality and morbidity in HIV-infected patients, but some are associated with cardiovascular complications, including endothelial dysfunction, an early marker for atherosclerosis. Our prior studies demonstrated that co-treatment of cells with an antioxidant therapy reversed NRTI-induced endothelial injury. Thus, as a proof of concept that mitochondrially-targeted antioxidants may be useful in preventing NRTI toxicity, in the current study, mice overexpressing a mitochondrial antioxidant, manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), were compared with wild-type (WT) mice. Mice were treated chronically with either zidovudine (AZT), lamivudine (3TC), or tenofovir (TDF) to determine whether overexpression of MnSOD protected them from endothelial dysfunction. Endothelial function was assessed using vessel reactivity experiments on thoracic aortas as well as measures of endothelium derived factors nitric oxide (NO), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and prostacyclin. Oxidative stress was evaluated as levels of plasma 8-isoprostane. Alterations in vessel reactivity, NO, and ET-1 in WT mice treated with AZT or 3TC were noted. Overexpression of MnSOD offered protection from decreases in vessel reactivity and increases in ET-1. These findings indicate that mitochondrial oxidative stress induced by AZT or 3TC plays a major role in mediating NRTI-induced endothelial dysfunction, and suggest that the use of targeted antioxidants administered in conjunction with NRTIs may attenuate these effects.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Atherosclerosis; Endothelial dysfunction; NRTI.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transplacentally exposed human and monkey newborn infants show similar evidence of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-induced mitochondrial toxicity.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007 Apr-May;48(3-4):201-9. doi: 10.1002/em.20201. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007. PMID: 16538687
-
Longer prior exposure to zidovudine/lamivudine-containing combination antiretroviral therapy, age, and male gender are each associated with reduced subcutaneous adipose tissue.HIV Clin Trials. 2012 Mar-Apr;13(2):103-10. doi: 10.1310/hct1302-103. HIV Clin Trials. 2012. PMID: 22510357
-
Mitochondrial toxicity in hearts of CD-1 mice following perinatal exposure to AZT, 3TC, or AZT/3TC in combination.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007 Apr-May;48(3-4):190-200. doi: 10.1002/em.20191. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007. PMID: 16395692
-
Quadruple nucleoside therapy with zidovudine, lamivudine, abacavir and tenofovir in the treatment of HIV.Antivir Ther. 2007;12(5):695-703. Antivir Ther. 2007. PMID: 17713153 Review.
-
Endothelial mitochondrial senescence accelerates cardiovascular disease in antiretroviral-receiving HIV patients.Toxicol Lett. 2019 Dec 15;317:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.09.018. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Toxicol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31562912 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Spirulina platensis to Ameliorate the Adverse Effects of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART).Nutrients. 2022 Jul 27;14(15):3076. doi: 10.3390/nu14153076. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35893930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consequences of Disturbing Manganese Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14959. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914959. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spirulina platensis Ameliorates Oxidative Stress Associated with Antiretroviral Drugs in HepG2 Cells.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;11(22):3143. doi: 10.3390/plants11223143. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432871 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic identification of cryostress in epididymal spermatozoa.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016 Nov 21;7:67. doi: 10.1186/s40104-016-0128-2. eCollection 2016. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27895910 Free PMC article.
-
The Essential Element Manganese, Oxidative Stress, and Metabolic Diseases: Links and Interactions.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Apr 5;2018:7580707. doi: 10.1155/2018/7580707. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29849912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adaramoye OA, Adewumi OM, Adesanoye OA, Faokunla OO, Farombi EO. Effect of tenofovir, an antiretroviral drug, on hepatic and renal functional indices of Wistar rats: protective role of vitamin E. Journal of basic and clinical physiology and pharmacology. 2012;23:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Beg S, Javed S, Kohli K. Bioavailability enhancement of coenzyme Q10: an extensive review of patents. Recent patents on drug delivery & formulation. 2010;4:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Bohm F, Pernow J. The importance of endothelin-1 for vascular dysfunction in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular research. 2007;76:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Brown KA, Didion SP, Andresen JJ, Faraci FM. Effect of aging, MnSOD deficiency, and genetic background on endothelial function: evidence for MnSOD haploinsufficiency. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2007;27:1941–1946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

