Surgery for stress urinary incontinence due to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery
- PMID: 25261861
- PMCID: PMC7105906
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008306.pub3
Surgery for stress urinary incontinence due to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery
Abstract
Background: Incontinence after prostatectomy for benign or malignant disease is a well-known and often a feared outcome. Although small degrees of incidental incontinence may go virtually unnoticed, larger degrees of incontinence can have a major impact on a man's quality of life.Conceptually, post-prostatectomy incontinence may be caused by sphincter malfunction or bladder dysfunction, or both. Most men with post-prostatectomy incontinence (60% to 100%) have stress urinary incontinence, which is involuntary urinary leakage on effort or exertion, or on sneezing or coughing. This may be due to intrinsic sphincter deficiency and may be treated with surgery for optimal management of incontinence. Detrusor dysfunction is more common after surgery for benign prostatic disease.
Objectives: To determine the effects of surgical treatment for urinary incontinence related to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery for:- men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) - transurethral resection of prostate (TURP), photo vaporisation of the prostate, laser enucleation of the prostate or open prostatectomy - and- men with prostate cancer - radical prostatectomy (retropubic, perineal, laparoscopic, or robotic).
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Register, which contains trials identified from Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, MEDLINE in process, ClinicalTrials.gov, and handsearching of journals and conference proceedings (searched 31 March 2014); MEDLINE (January 1966 to April 2014); EMBASE (January 1988 to April 2014); and LILACS (January 1982 to April 2014). We handsearched the reference lists of relevant articles and conference proceedings. We contacted investigators to locate studies.
Selection criteria: Randomised or quasi-randomised trials that include surgical treatments of urinary incontinence after prostate surgery.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently screened the trials identified, appraised quality of papers, and extracted data.
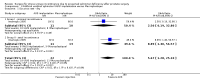
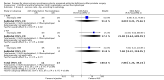
Main results: Only one study with 45 participants met the inclusion criteria. Men were divided in two sub-groups (minimal or total incontinence) and each group was randomised to artificial urethral sphincter (AUS) implantation or Macroplastique injection. Follow-up ranged from six to 120 months. In the trial as a whole, the men treated with AUS were more likely to be dry (18/20, 82%) than those who had the injectable treatment (11/23, 46%) (odds ratio (OR) 5.67, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.28 to 25.10). However, this effect was only statistically significant for the men with more severe ('total') incontinence (OR 8.89, 95% CI 1.40 to 56.57) and the CIs were wide. There were more severe complications in the group undergoing AUS, and the costs were higher. AUS implantation was complicated in 5/22 (23%) men: the implant had to be removed from one man because of infection and in one man due to the erosion of the cuff, in one man the pump was changed due to mechanical failure, in one man there was migration to the intraperitoneal region, and one man experienced scrotal erosion. In the injectable group, 3/23 (13%) men had a complication: one man treated with Macroplastique injection had to be catheterised because of urinary retention and two men developed urinary tract infections.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence available at present was of very low quality because we identified only one small randomised clinical trial. Although the result was favourable for the implantation of AUS in the group with severe incontinence, this result should be considered with caution due to the small sample size and uncertain methodological quality of the study found.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the review authors had a direct financial interest, paid consultancy or share‐holding in a company producing the intervention(s) under review or a rival treatment.
Figures






Update of
-
Surgery for stress urinary incontinence due to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Apr 13;(4):CD008306. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008306.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 27;(9):CD008306. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008306.pub3. PMID: 21491408 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Imamoglu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Imamoglu MA, Tuygun C, Bakirtas H, Yigitbasi O, Kiper A. The comparison of artificial urinary sphyncter implantation and endourethral macroplastique injection for the treatment of postprostatectomy incontinence. European Urology 2005;47:209‐13. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Altinova 2009 {published data only}
-
- Altinova S, Demirci DA, Ozdemir AT, Akbulut Z, Atmaca AF, Caglayan A, et al. Incorporation of anterior rectus fascial sling into radical retropubic prostatectomy improves postoperative continence. Urologia Internationalis 2009;83(1):19‐21. [SRINCONT32094] - PubMed
Lima 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lima JPC, Pompeo ACL, Bezerra CA. Sub urethral sling for male urinary incontinence: randomized clinic trial of two slings. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2013;32(6):894‐5. [sr‐incont49193]
Noguchi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Noguchi M, Kakuma T, Suekane S, Nakashima O, Mohamed ER, Matsuoka K. A randomized clinical trial of suspension technique for improving early recovery of urinary continence after radical retropubic prostatectomy. BJU International 2008;102(8):958‐63. [SRINCONT27722] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Abrams 2014 {unpublished data only}
-
- Abrams P. Male synthetic sling versus Artificial urinary Sphincter Trial for men with urodynamic stress incontinence after prostate surgery: Evaluation by Randomised controlled trial (MASTER), 2014. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN49212975/MASTER (accessed 23 September 2014). [sr‐incont60070]
Haab 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Haab F. Prospective, Randomized, Multicentric, Comparative Trial of Two Devices in Surgical Treatment of Post‐radical Prostatectomy Stress Urinary Incontinence: Periurethral Pro‐ACT(TM) Balloons and AdvanceXP(TM) Retrourethral Male Sling. clinicaltrials gov/show/NCT01500603 (accessed 23 September 2014). [srincont60065]
Ockrim 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ockrim J, Kass‐Iliyya A. Single‐site, two‐arm randomised controlled study: a comparison of effectiveness of the Advance male sling and AMS 800 artificial urinary sphincter for mild to moderate post prostatectomy incontinence. www controlled‐trials com/ISRCTN55599282 (accessed 23 September 2014). [srincont50321]
Additional references
Abrams 1991
-
- Abrams PH. Investigation of post prostatectomy problems. Urology 1991;15:209‐12. - PubMed
Abrams 2003
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P. The standardization of terminology in lower urinary tract function: report from the standardization sub‐committee of the international continence society. Urology 2003;61:37‐41. - PubMed
Albertsen 1997
-
- Albertsen PC, Lu‐Yao GL, Warren J. Risk of complication and readmission associated with radical prostatectomy in community practice: a Medicare claims analysis. Journal of Urology 1997;157:93.
Armstrong 2009
Augustin 2002
-
- Augustin H, Pummer K, Daghofer F, Habermann H, Primus G, Hubmer G. Patient self‐reporting questionnaire on urological morbidity and bother after radical retropubic prostatectomy. European Urology 2002;42:112‐7. - PubMed
Bauer 2009
-
- Bauer RM, Bastian PJ, Gozzi C, Stief CG. Postprostatectomy Incontinence: all about diagnosis and management. European Urology 2009;55:322‐33. - PubMed
Black 2006
-
- Black L, Naslund MJ, Gilbert TD, Davis AE, Ollendorf DA. An examination of treatment patterns and costs of care among patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. American Journal of Managed Care 2006;12(4):S99‐110. - PubMed
Burkhard 2006
-
- Burkhard FC, Kessler TM, Fleischmann A, Thalmann GN, Schumacher M, Studer UE. Nerve‐sparing open radical retropubic prostatectomy? Does it have an impact on urinary continence?. Journal of Urology 2006;176:189‐95. - PubMed
Campbell 2012
Catalona 1999
-
- Catalona WJ, Carvalhal GF, Mager DE, Smith DS. Potency, continence and complication rates in 1,870 consecutive radical retropubic prostatectomies. Journal of Urology 1999;162:433‐8. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. . . .
Eastham 1996
-
- Eastham JA, Kattan MW, Rogers E, Goad JR, Ohori M, Boone TB, et al. Risk factors for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Journal of Urology 1996;156:1707‐13. - PubMed
Fader 2008
Filocamo 2007
-
- Filocamo M, Li Marzi V, Popolo G, Cecconi F, Villari D, Marzocco M, et al. Pharmacologic treatment in postprostatectomy stress urinary incontinence. European Urology 2007;51:1559‐64. - PubMed
Foote 1991
-
- Foote J, Yun S, Leach GE. Post‐prostatectomy incontinence. Pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Urology Clinics of North America 1991;18(2):229‐41. - PubMed
García Montes 2007
-
- García Montes F, Knight SL, Greenwell T, Mundy AR, Craggs MD. "Flowsecure" artificial urinary sphincter: a new adjustable artificial urinary sphincter concept with conditional occlusion for stress urinary incontinence [Esfínter Urinario Artificial “FlowSecureTM”: Un nuevo concepto de esfínter artificial regulable y con oclusión condicional para la incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo]. Actas Urol Esp 2007;31(7):752‐8. - PubMed
Haab 1996
-
- Haab F, Yamaguchi R, Leach GE. Postprostatectomy incontinence. Urology Clinics of North America 1996;23:447‐57. - PubMed
Hammerer 1997
-
- Hammerer P, Huland H. Urodynamic evaluation of changes in urinary control after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Journal of Urology 1997;157:233‐6. - PubMed
Herr 1994
-
- Herr HW. Quality of life of incontinence men after radical prostatectomy. Journal of Urology 1994;151:652. - PubMed
Herschorn 2010
-
- Herschorn S, Bruschini H, Comiter C, Grise P, Hanus T, Kirschner‐Hermanns R, et al. Surgical treatment of stress incontinence in men. Neurology and Urodynamics 2010;29:179‐90. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
ICI 2008
-
- International Consultation on Incontinence. Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence (ICI) ‐ Surgery for Urinary Incontinence in Men Committee highlights. 2008 July 5‐8; Paris.
Jack 2005
-
- Jack GS, Almeida GF, Zhang R, Alfonso ZC, Zuk PA, Rodriguez LV. Processed lipoaspirate cells for tissue engineering of the lower urinary tract: implications for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence and bladder reconstruction. Journal of Urology 2005;174(5):2041‐5. - PubMed
Kundu 2004
-
- Kundu SD, Roehl KA, Eggener SE, Antenor JAV, Han M, Catalona WJ. Potency, continence and complications in 3,477 consecutive radical retropubic prostatectomies. Journal of Urology 2004;172:2227‐31. - PubMed
Ogah 2009
Onur 2004
-
- Onur R, Rajpurkar A, Singla A. New perineal bone anchored male sling: lessons learned. Urology 2004;64:58‐61. - PubMed
Penson 2005
-
- Penson DF, McLerran D, Feng Z, Li L, Albertsen PC, Gilliland FC, et al. Five‐year urinary and sexual outcomes after radical prostatectomy: results from the prostate cancer outcomes study. Journal of Urology 2005;173:1701‐5. - PubMed
Peyromaure 2002
-
- Peyromaure M, Ravery V, Boccon‐Gibod L. The management of stress urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. British Journal of Urology International 2002;90:155‐61. - PubMed
Raz 1992
-
- Raz S, Erickson DR. SEAPI QMM incontinence classification system. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1992;11(3):187‐99. - PubMed
Reference Manager 2012 [Computer program]
-
- Thomson Reuters. Reference Manager Professional Edition. Version 12. New York: Thomson Reuters, 2012.
Rehder 2007
-
- Rehder P, Gozzi C. Transobturator sling suspension for male urinary incontinence including post‐radical prostatectomy. European Urology 2007;52(3):860‐7. - PubMed
Sacco 2006
-
- Sacco E, Prayer‐Galetti T, Pinto F, Fracalanza S, Betto G, Pagano F, et al. Urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: incidence by definition, risk factors and temporal trend in a large series with a long‐term follow‐up. British Journal of Urology International 2006;97:1234‐41. - PubMed
Sanda 2008
-
- Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, Sandler HM, Northouse L, Hembroff L, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate‐cancer survivors. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358:1250‐61. - PubMed
Schlenker 2006
-
- Schlenker B, Gratzke C, Reich O, Schorsch I, Seitz M, Stief CG. Preliminary results on the off‐label use of duloxetine for the treatment of stress incontinence after radical prostatectomy or cystectomy. European Urology 2006;49:1075‐8. - PubMed
Secin 2005
-
- Secin FP, Martinez‐Salamanca JI, Eilber KS. Limited efficacy of permanent injectable agents in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Archivos Espanoles de Urologia 2005;58(5):431‐6. - PubMed
Seckiner 2007
-
- Seckiner I, Yesilli C, Mungan NA, Aykanat A, Akduman B. Correlations between the ICIQ‐SF score and urodynamic findings. Neurourology & Urodynamics 2007;26:492‐4. - PubMed
Sierra 2006
-
- Sierra JM, Romano SV, Romo IG, Ortega JB, Casado JS, Moyano AS. New male sling "Argus" for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Archivos Espanoles de Urologia 2006;59:607‐13. - PubMed
Stamey 1981
-
- Stamey TA. Endoscopic suspension of the vesical neck for surgically curable incontinence in the female. Monograph in Urology 1981;2(3):387‐90.
Steiner 1991
-
- Steiner MS, Morton RA, Walsh PC. Impact of anatomical radical prostatectomy on urinary continence. Journal of Urology 1991;145:512‐5. - PubMed
Ullrich 2004
-
- Ullrich NFE, Comiter CV. The male sling for stress urinary incontinence: urodynamic and subjective assessment. Journal of Urology 2004;172:204‐6. - PubMed
van der Horst 2007
-
- Horst C, Naumann CM, Al‐Najaar A, Seif C, Stubinger SH, Junemann KP, et al. Etiology and pathophysiology of male stress incontinence. Urologe A 2007;46:229‐41. - PubMed
Veenema 1977
-
- Veenema RJ, Gursel EO, Lattimer JK. Radical retropubic prostatectomy for cancer: a 20‐year experience. Journal of Urology 1977;117:330‐1. - PubMed
Walsh 1980
-
- Walsh PC, Jewett HJ. Radical surgery for prostatic cancer. Cancer 1980;45(7 Suppl):1906‐11. - PubMed
Walsh 1994
-
- Walsh PC, Partin AW, Epstein JI. Cancer control and QoL following anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy: results at 10 years. Journal of Urology 1994;152:1831‐6. - PubMed
Walsh 2000
-
- Walsh PC, Marschke P, Ricker D, Burnett AL. Patient reported urinary continence and sexual function after anatomic radical prostatectomy. Urology 2000;55:58‐61. - PubMed
Wei 2000
-
- Wei JT, Montie JE. Comparison of patients and physicians rating of urinary incontinence following radical prostatectomy. Seminars in Urologic Oncology 2000;18:76‐80. - PubMed
Zahariou 2006
-
- Zahariou A, Papaioannou P, Kalogirou G. Is HCl duloxetine effective in the management of urinary stress incontinence after radical prostatectomy?. Urology International 2006;77:9‐12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

