Effects of β-sitosterol derived from Artemisia capillaris on the activated human hepatic stellate cells and dimethylnitrosamine-induced mouse liver fibrosis
- PMID: 25262005
- PMCID: PMC4193130
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-363
Effects of β-sitosterol derived from Artemisia capillaris on the activated human hepatic stellate cells and dimethylnitrosamine-induced mouse liver fibrosis
Abstract
Background: β-sitosterol is a cholesterol-like phytosterol, which widely distributed in the plant kingdom. Here, anti-fibrotic effect of the β-sitosterol was studied using the activated human hepatic stellate cell (HSC) model and dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced mouse hepatic fibrosis model.
Method: HSCs were activated by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and the collagen-1 and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expressions were measured at the mRNA and protein level. We also studied the effect β-sitosterol using DMN-induced mouse hepatic fibrosis model. We then measured the collagen-1 and α-SMA expression levels in vivo to investigate anti-hepatofibrotic effect of β-sitosterol, at both of the mRNA and protein level.
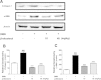
Results: β-sitosterol down regulated the mRNA and protein expression levels of collagen-1 and α-SMA in activated HSC. Oral administration of the β-sitosterol successfully alleviated the DMN-induced mouse liver damage and prevented collagen accumulation. The mRNA and protein expression levels of collagen-1 and α-SMA were also down regulated in β-sitosterol treated mouse group.
Conclusions: This study shows the effect of β-sitosterol on the TGF-β -or DMN-induced hepatofibrosis. Hence, we demonstrate the β-sitosterol as a potential therapeutic agent for the hepatofibrosis.
Figures



References
-
- Poynard T, Mathurin P, Lai CL, Guyader D, Poupon R, Tainturier MH, Myers RP, Muntenau M, Ratziu V, Manns M, Vogel A, Capron F, Chedid A, Bedossa P, Panfibrosis Group A comparison of fibrosis progression in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2003;38(3):257–265. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(02)00413-0. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/363/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

