Negative T wave in ischemic heart disease: a consensus article
- PMID: 25262662
- PMCID: PMC6932621
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.12193
Negative T wave in ischemic heart disease: a consensus article
Abstract
Background: For many years was considered that negative T wave in ischemic heart disease represents ischemia and for many authors located in subepicardial area.
Methods: We performed a review based in the literature and in the experience of the authors commenting the real significance of the presence of negative T wave in patients with ischemic heart disease.
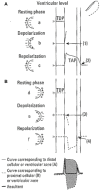
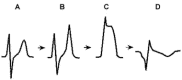
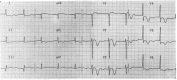
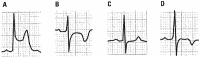
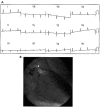
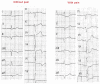
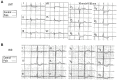
Results: The negative T wave may be of primary or secondary type. Negative T wave observed in ischemic heart disease are of primary origin, therefore not a consequence of abnormal repolarization pattern. The negative T wave of ischemic origin presents the following characteristics: (1) are symmetrical and of variable deepness; (2) present mirror patterns; (3) starts in the second part of repolarization; and (4) may be accompanied by positive or negative U wave. The negative T wave of ischemic origin may be seen in the following clinical settings: (1) postmyocardial infarction due to a window effect of necrotic zone and (2) as a consequence of reperfusion in case of aborted MI when the artery has opened spontaneously, or after fibrinolysis, PCI, or coronary spasm.
Conclusion: Acute ongoing ischemia do not cause negative T wave. This pattern appears when the ongoing ischemia is vanishing or in the chronic phase. In all these cases the cause of negative T wave is not located in the subepicardial area. Furthermore, positive exercise testing is expressed by ST depression never by isolated negative T wave. There are many circumstances that may present negative T wave outside ischemic heart disease and that have been discussed in this paper.
Keywords: electrocardiography; ischemic heart disease; negative T wave.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures











References
-
- Rosenbaum FF, Wilson FN, Johnston FD. The precordial electrocardiogram in high lateral myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 1946;32:135–151. - PubMed
-
- Burgess JM, Green LS, Millar D, et al. The sequence of normal ventricular recovery. Am Heart J 1972;84:660–169. - PubMed
-
- Ashman R, Hull E. Essentials of Electrocardiography. Macmillan Co. New York 1937.
-
- Burnes J, Waldo A, Rudy Y. Imaging dispersion of ventricular repolarization. Circulation 2001;104:1299–1305. - PubMed
-
- Franz MR, Bargheer K, Rafflenbeul W, Haverich A, Lichtlen PR. Monophasic action potential mapping in human subjects with normal electrocardigrams: Direct evidence of the T wave. Circulation 1987;75:379–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

