Amygdala enlargement in unaffected offspring of bipolar parents
- PMID: 25263277
- PMCID: PMC4254042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.08.023
Amygdala enlargement in unaffected offspring of bipolar parents
Abstract
Background: Bipolar disorder (BD) is a devastating disorder with a strong genetic component. While the frontolimbic profile of individuals suffering from BD is relatively well-established, there is still disagreement over the neuroanatomical features of unaffected BD offspring.
Material and methods: Brain volumetric measures were obtained for 82 children and adolescents including 18 unaffected BD offspring (10.50 ± 3.37 years), 19 BD offspring suffering from psychiatric disorders (12.87 ± 3.28 years) and 45 healthy controls (HC-10.50 ± 3.37 years). Clinical diagnoses were established according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) criteria. Cortical reconstruction and volumetric segmentation were performed with the Freesurfer image analysis suite. Profile analyses compared frontolimbic volumes across groups. Age, gender, testing site, ethnicity and intracranial volume were entered as covariates.
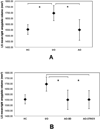
Results: The right amygdala was significantly larger in unaffected BD offspring compared to BD offspring with psychiatric disorders and HC. Volumes of striatal, hippocampal, cingulate, and temporal regions were comparable across groups.
Discussion: The size of the amygdala may be a marker of disease susceptibility in offspring of BD parents. Longitudinal studies are needed to examine rates of conversion to BD as related to specific pre-morbid brain abnormalities.
Keywords: Amygdala; Bipolar disorder; Freesurfer; Offspring; Volume.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosures
Drs Bauer, Suchting, Green, El Fangary and Zunta-Soares have no conflicts of interest
Figures
References
-
- Mathers CD, Fat DM, Boerma J. World Health Organization; 2008. The global burden of disease: 2004 update.
-
- Craddock N, Sklar P. Genetics of bipolar disorder. The Lancet. 2013;381(9878):1654–1662. - PubMed
-
- Kieseppa T, Tuulio-Henriksson A, Haukka J, Van Erp T, Glahn D, Cannon TD, et al. Memory and verbal learning functions in twins with bipolar-I disorder, and the role of information-processing speed. Psychological medicine. 2005;35(2):205–215. - PubMed
-
- McGuffin P, Rijsdijk F, Andrew M, Sham P, Katz R, Cardno A. The heritability of bipolar affective disorder and the genetic relationship to unipolar depression. Archives of general psychiatry. 2003;60(5):497–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

