SDF-1 inhibition targets the bone marrow niche for cancer therapy
- PMID: 25263552
- PMCID: PMC4194173
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.042
SDF-1 inhibition targets the bone marrow niche for cancer therapy
Abstract
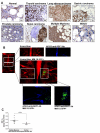
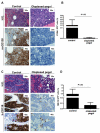
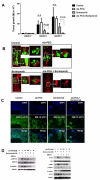
Bone marrow (BM) metastasis remains one of the main causes of death associated with solid tumors as well as multiple myeloma (MM). Targeting the BM niche to prevent or modulate metastasis has not been successful to date. Here, we show that stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1/CXCL12) is highly expressed in active MM, as well as in BM sites of tumor metastasis and report on the discovery of the high-affinity anti-SDF-1 PEGylated mirror-image l-oligonucleotide (olaptesed-pegol). In vivo confocal imaging showed that SDF-1 levels are increased within MM cell-colonized BM areas. Using in vivo murine and xenograft mouse models, we document that in vivo SDF-1 neutralization within BM niches leads to a microenvironment that is less receptive for MM cells and reduces MM cell homing and growth, thereby inhibiting MM disease progression. Targeting of SDF-1 represents a valid strategy for preventing or disrupting colonization of the BM by MM cells.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Azab AK, Runnels JM, Pitsillides C, Moreau AS, Azab F, Leleu X, Jia X, Wright R, Ospina B, Carlson AL, et al. CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100 disrupts the interaction of multiple myeloma cells with the bone marrow microenvironment and enhances their sensitivity to therapy. Blood. 2009;113:4341–4351. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bryden AA, Islam S, Freemont AJ, Shanks JH, George NJ, Clarke NW. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide: expression in prostate cancer bone metastases. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2002;5:59–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

