Loss of MBNL leads to disruption of developmentally regulated alternative polyadenylation in RNA-mediated disease
- PMID: 25263597
- PMCID: PMC4224598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.027
Loss of MBNL leads to disruption of developmentally regulated alternative polyadenylation in RNA-mediated disease
Abstract
Inhibition of muscleblind-like (MBNL) activity due to sequestration by microsatellite expansion RNAs is a major pathogenic event in the RNA-mediated disease myotonic dystrophy (DM). Although MBNL1 and MBNL2 bind to nascent transcripts to regulate alternative splicing during muscle and brain development, another major binding site for the MBNL protein family is the 3' untranslated region of target RNAs. Here, we report that depletion of Mbnl proteins in mouse embryo fibroblasts leads to misregulation of thousands of alternative polyadenylation events. HITS-CLIP and minigene reporter analyses indicate that these polyadenylation switches are a direct consequence of MBNL binding to target RNAs. Misregulated alternative polyadenylation also occurs in skeletal muscle in a mouse polyCUG model and human DM, resulting in the persistence of neonatal polyadenylation patterns. These findings reveal an additional developmental function for MBNL proteins and demonstrate that DM is characterized by misregulation of pre-mRNA processing at multiple levels.
Figures
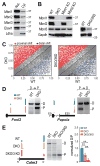
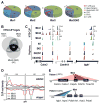

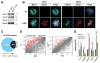
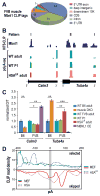

References
-
- Arnold ES, Ling SC, Huelga SC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Ditsworth D, Kordasiewicz HB, McAlonis-Downes M, Platoshyn O, Parone PA, et al. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:E736–745. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen TJ, Waddell DS, Barrientos T, Lu Z, Feng G, Cox GA, Bodine SC, Yao TP. The histone deacetylase HDAC4 connects neural activity to muscle transcriptional reprogramming. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:33752–33759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

