Dysregulated serum response factor triggers formation of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25266280
- PMCID: PMC4365683
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.27539
Dysregulated serum response factor triggers formation of hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
- Hepatology. 2015 May;61(5):1772. Authenrieth, Stella E [corrected to Autenrieth, Stella E]
Abstract
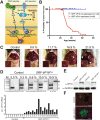
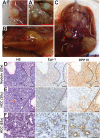
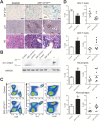
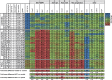
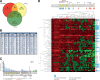
The ubiquitously expressed transcriptional regulator serum response factor (SRF) is controlled by both Ras/MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and Rho/actin signaling pathways, which are frequently activated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We generated SRF-VP16iHep mice, which conditionally express constitutively active SRF-VP16 in hepatocytes, thereby controlling subsets of both Ras/MAPK- and Rho/actin-stimulated target genes. All SRF-VP16iHep mice develop hyperproliferative liver nodules that progresses to lethal HCC. Some murine (m)HCCs acquire Ctnnb1 mutations equivalent to those in human (h)HCC. The resulting transcript signatures mirror those of a distinct subgroup of hHCCs, with shared activation of oncofetal genes including Igf2, correlating with CpG hypomethylation at the imprinted Igf2/H19 locus.
Conclusion: SRF-VP16iHep mHCC reveal convergent Ras/MAPK and Rho/actin signaling as a highly oncogenic driver mechanism for hepatocarcinogenesis. This suggests simultaneous inhibition of Ras/MAPK and Rho/actin signaling as a treatment strategy in hHCC therapy.
© 2014 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc., on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Boyault S, Rickman DS, de Reynies A, Balabaud C, Rebouissou S, Jeannot E, et al. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology. 2007;45:42–52. - PubMed
-
- Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M, Conner EA, Lee JS, et al. Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1117–1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
