Polo-like kinase 3 regulates CtIP during DNA double-strand break repair in G1
- PMID: 25267294
- PMCID: PMC4178966
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201401146
Polo-like kinase 3 regulates CtIP during DNA double-strand break repair in G1
Abstract
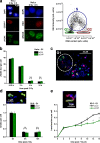
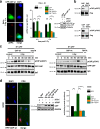
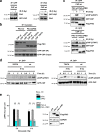
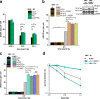
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homologous recombination (HR). The C terminal binding protein-interacting protein (CtIP) is phosphorylated in G2 by cyclin-dependent kinases to initiate resection and promote HR. CtIP also exerts functions during NHEJ, although the mechanism phosphorylating CtIP in G1 is unknown. In this paper, we identify Plk3 (Polo-like kinase 3) as a novel DSB response factor that phosphorylates CtIP in G1 in a damage-inducible manner and impacts on various cellular processes in G1. First, Plk3 and CtIP enhance the formation of ionizing radiation-induced translocations; second, they promote large-scale genomic deletions from restriction enzyme-induced DSBs; third, they are required for resection and repair of complex DSBs; and finally, they regulate alternative NHEJ processes in Ku(-/-) mutants. We show that mutating CtIP at S327 or T847 to nonphosphorylatable alanine phenocopies Plk3 or CtIP loss. Plk3 binds to CtIP phosphorylated at S327 via its Polo box domains, which is necessary for robust damage-induced CtIP phosphorylation at S327 and subsequent CtIP phosphorylation at T847.
© 2014 Barton et al.
Figures




References
-
- Beucher, A., Birraux J., Tchouandong L., Barton O., Shibata A., Conrad S., Goodarzi A.A., Krempler A., Jeggo P.A., and Löbrich M.. 2009. ATM and Artemis promote homologous recombination of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in G2. EMBO J. 28:3413–3427 10.1038/emboj.2009.276 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

