Phospholipase cε, an effector of ras and rap small GTPases, is required for airway inflammatory response in a mouse model of bronchial asthma
- PMID: 25269075
- PMCID: PMC4182471
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108373
Phospholipase cε, an effector of ras and rap small GTPases, is required for airway inflammatory response in a mouse model of bronchial asthma
Abstract
Background: Phospholipase Cε (PLCε) is an effector of Ras and Rap small GTPases and expressed in non-immune cells. It is well established that PLCε plays an important role in skin inflammation, such as that elicited by phorbol ester painting or ultraviolet irradiation and contact dermatitis that is mediated by T helper (Th) 1 cells, through upregulating inflammatory cytokine production by keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts. However, little is known about whether PLCε is involved in regulation of inflammation in the respiratory system, such as Th2-cells-mediated allergic asthma.
Methods: We prepared a mouse model of allergic asthma using PLCε+/+ mice and PLCεΔX/ΔX mutant mice in which PLCε was catalytically-inactive. Mice with different PLCε genotypes were immunized with ovalbumin (OVA) followed by the challenge with an OVA-containing aerosol to induce asthmatic response, which was assessed by analyzing airway hyper-responsiveness, bronchoalveolar lavage fluids, inflammatory cytokine levels, and OVA-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) levels. Effects of PLCε genotype on cytokine production were also examined with primary-cultured bronchial epithelial cells.
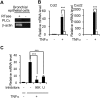
Results: After OVA challenge, the OVA-immunized PLCεΔX/ΔX mice exhibited substantially attenuated airway hyper-responsiveness and broncial inflammation, which were accompanied by reduced Th2 cytokine content in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluids. In contrast, the serum levels of OVA-specific IgGs and IgE were not affected by the PLCε genotype, suggesting that sensitization was PLCε-independent. In the challenged mice, PLCε deficiency reduced proinflammatory cytokine production in the bronchial epithelial cells. Primary-cultured bronchial epithelial cells prepared from PLCεΔX/ΔX mice showed attenuated pro-inflammatory cytokine production when stimulated with tumor necrosis factor-α, suggesting that reduced cytokine production in PLCεΔX/ΔX mice was due to cell-autonomous effect of PLCε deficiency.
Conclusions: PLCε plays an important role in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma through upregulating inflammatory cytokine production by the bronchial epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


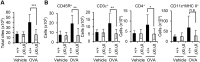



Similar articles
-
Phospholipase Cε plays a crucial role in neutrophilic inflammation accompanying acute lung injury through augmentation of CXC chemokine production from alveolar epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2019 Jan 11;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0975-4. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 30634975 Free PMC article.
-
4-1 BB stimulation inhibits allergen-specific immunoglobulin E production and airway hyper-reactivity but partially suppresses bronchial eosinophilic inflammation in a mouse asthma model.Clin Exp Allergy. 2006 Mar;36(3):377-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02445.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16499650
-
Crucial role of phospholipase Cepsilon in induction of local skin inflammatory reactions in the elicitation stage of allergic contact hypersensitivity.J Immunol. 2010 Jan 15;184(2):993-1002. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901816. Epub 2009 Dec 9. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20007527
-
Key mediators in the immunopathogenesis of allergic asthma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Nov;23(1):316-29. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.034. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24933589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bronchial epithelium in children: a key player in asthma.Eur Respir Rev. 2016 Jun;25(140):158-69. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0101-2015. Eur Respir Rev. 2016. PMID: 27246593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of PLCε inhibits inflammatory cytokine release via STAT3 phosphorylation in human bladder cancer cells.Tumour Biol. 2015 Dec;36(12):9723-32. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3712-8. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26156799
-
Phospholipase C epsilon-1 (PLCƐ1) mediates macrophage activation and protection against tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2024 Apr 9;92(4):e0049523. doi: 10.1128/iai.00495-23. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38451080 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of JTE013 abrogates experimental asthma by regulating proinflammatory cytokine production from bronchial epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2016 Nov 9;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0465-x. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27829417 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase Cε plays a crucial role in neutrophilic inflammation accompanying acute lung injury through augmentation of CXC chemokine production from alveolar epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2019 Jan 11;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0975-4. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 30634975 Free PMC article.
-
The controversial role of phospholipase C epsilon (PLCε) in cancer development and progression.J Cancer. 2017 Feb 25;8(5):716-729. doi: 10.7150/jca.17779. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28382133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holgate ST (2012) Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat Med 18: 673–683. - PubMed
-
- Lambrecht BN, Hammad H (2012) The airway epithelium in asthma. Nat Med 18: 684–692. - PubMed
-
- Suh PG, Park JI, Manzoli L, Cocco L, Peak JC, et al. (2008) Multiple roles of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C isozymes. BMB Rep 41: 415–434. - PubMed
-
- Lopez I, Mak EC, Ding J, Hamm HE, Lomasney JW (2001) A novel bifunctional phospholipase c that is regulated by Gα12 and stimulates the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 2758–2765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

