Interleukin-10: a pleiotropic regulator in pregnancy
- PMID: 25269386
- PMCID: PMC4382460
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.12329
Interleukin-10: a pleiotropic regulator in pregnancy
Abstract
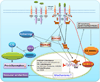
Pregnancy is a unique and well-choreographed physiological process that involves intricate interplay of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory milieu, hormonal changes, and cellular and molecular events at the maternal-fetal interface. IL-10 is a pregnancy compatible cytokine that plays a vital role in maintaining immune tolerance. A wide array of cell types including both immune and non-immune cells secret IL-10 in an autocrine and paracrine manner. IL-10 binds to a specific receptor complex and activates JAK-STAT and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways while inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. IL-10 exerts its anti-inflammatory effects mainly by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α, by inducing heme oxygenase-1, and by inhibiting antigen presentation via blocking major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II expression. Prior studies from our group and others have shown that IL-10 also functions as a potent protector against vascular dysfunction, and enhancement of IL-10 may serve as an immunotherapeutic intervention to treat adverse pregnancy outcomes. This review seeks to critically evaluate the archetypal functions of IL-10 as an immune suppressive factor as well as its novel functions as a vascular protector and modulator of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and autophagy in the context of normal and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Keywords: Adverse pregnancy outcomes; angiogenesis; autophagy; endoplasmic reticulum stress; immune tolerance; preeclampsia.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Murphy SP, Sharma S. IL-10 and pregnancy. In: Gil Mor., editor. Immunology of Pregnancy. NY: Springer Science; 2004. pp. 26–36.
-
- Dealtry GB, O'Farrell MK, Fernandez N. The Th2 cytokine environment of the placenta. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000;123(2):107–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

