Xuebijing exerts protective effects on lung permeability leakage and lung injury by upregulating Toll-interacting protein expression in rats with sepsis
- PMID: 25269519
- PMCID: PMC4214342
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1943
Xuebijing exerts protective effects on lung permeability leakage and lung injury by upregulating Toll-interacting protein expression in rats with sepsis
Abstract
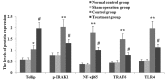
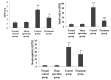
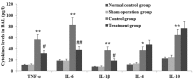
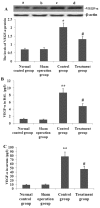
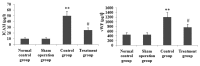
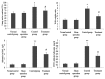
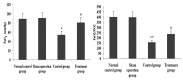
Xuebijing (XBJ) is a type of traditional Tibetan medicine, and previous pharmacological studies have shown that the ethanol extract is derived from Chuanxiong, Chishao, Danshen and Honghua. Chuanxiong, Chishao, Danshen and Honghua possesses potent anti-inflammatory activity, and has been used in the treatment of inflammatory infectious diseases. In the present study, we investigated the effects of XBJ on pulmonary permeability and lung injury in cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis in rats. A CLP sepsis model was established for the control and treatment groups, respectively. Approximately 2 h prior to surgery, an amount of 100 mg/kg XBJ injection was administered to the treatment group. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PT-PCR) and western blot analysis were used to examine the expression of Toll-interacting protein (Tollip), interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), nuclear factor-κB65 (NF-κB65) and TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) in lung tissue. ELISA was applied to detect changes of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and von wille-brand factor (vWF) in serum. The number of neutrophils, albumin and total cells in the BAL fluid were measured. For histological analysis, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains were evaluated. Lung permeability, the wet/dry weight ratio (W/D) and the lung pathology score were determined following the induction of ALI by CLP for 24 h. The results demonstrated that XBJ upregulated Tollip expression and blocked the activity of IRAK1, TLR4, NF-κβ65 and TRAF6. Additionally, the number of neutrophils and total cells were significantly decreased in the XBJ group compared to that in the control group. Lung permeability, the wet/dry weight ratio (W/D) and the lung pathology score were significantly decreased in the XBJ group. The histological results also demonstrated the attenuation effect of XBJ on CLP-induced lung inflammation. The results of the present study indicated that XBJ has a significantly reduced CLP-induced lung permeability by upregulating Tollip expression. The protective effects of XBJ suggest its therapeutic potential in CLP-induced acute lung injury treatment.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Protective effect of Xuebijing injection on D-galactosamine- and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury in rats through the regulation of p38 MAPK, MMP-9 and HO-1 expression by increasing TIPE2 expression.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Nov;38(5):1419-1432. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2749. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27666960 Free PMC article.
-
Xuebijing injection induces anti-inflammatory-like effects and downregulates the expression of TLR4 and NF-κB in lung injury caused by dichlorvos poisoning.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:1404-1411. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.111. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30119213
-
Discovery of Xuebijing Injection Exhibiting Protective Efficacy on Sepsis by Inhibiting the Expression of HMGB1 in Septic Rat Model Designed by Cecal Ligation and Puncture.Am J Ther. 2016 Nov/Dec;23(6):e1819-e1825. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000296. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 26313171
-
Obesity, inflammation, and lung injury (OILI): the good.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:978463. doi: 10.1155/2014/978463. Epub 2014 May 11. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24899788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic efficacy and mechanisms of Xuebijing in Acinetobacter baumannii infection based on meta-analysis and integrated pharmacology approaches.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 23;16:1598359. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1598359. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40487407 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Xuebijing Administration Alleviates Pulmonary Endothelial Inflammation and Coagulation Dysregulation in the Early Phase of Sepsis in Rats.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 11;11(22):6696. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226696. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431172 Free PMC article.
-
Xuebijing injection treatment inhibits vasopermeability and reduces fluid requirements in a canine burn model.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017 Dec;43(6):875-882. doi: 10.1007/s00068-016-0748-4. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017. PMID: 28070608
-
Marked Reduction in 28-day Mortality Among Elderly Patients with Severe Community-acquired Pneumonia: Post Hoc Analysis of a Large Randomized Controlled Trial.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Nov 9;15:2109-2115. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S268140. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 33204076 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacologic therapies of ARDS: From natural herb to nanomedicine.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;13:930593. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.930593. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36386221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xuebijing injection alleviates cytokine-induced inflammatory liver injury in CLP-induced septic rats through induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Sep;12(3):1531-1536. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3476. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27602076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ, Hudson LD. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Berthiaume Y, Folkesson HG, Matthay MA. Lung edema clearance: 20 years of progress invited review: alveolar edema fluid clearance in the injured lung. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93:2207–2213. - PubMed
-
- Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L, Martinon F, Plumpton C, Maschera B, Lewis A, Ray K, Tschopp J, Volpe F. Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:346–351. - PubMed
-
- Yamakami M, Yokosawa H. Tom1 (target of Myb 1) is a novel negative regulator of interleukin-1- and tumor necrosis factor-induced signaling pathways. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:564–566. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

