The production and distribution of IL-6 and TNF-a in subcutaneous adipose tissue and their correlation with serum concentrations in Welsh ponies with equine metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 25269712
- PMCID: PMC4367141
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.1.113
The production and distribution of IL-6 and TNF-a in subcutaneous adipose tissue and their correlation with serum concentrations in Welsh ponies with equine metabolic syndrome
Abstract
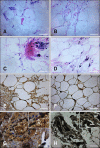
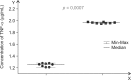
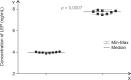
A main symptom of equine metabolic syndrome (EMS) in ponies is pathological obesity characterized by abnormal accumulation of fat deposits and inflammation. In this study, we analyzed the expression of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), in subcutaneous adipose tissue and the correlation with serum concentrations in peripheral blood of Welsh ponies. Based on clinical examination findings, the animals were divided into two groups: ponies affected with EMS (n = 8) and obese ponies (n = 8). The adipose tissue was examined using immunohistochemical analysis while concentrations IL-6 and TNF-a were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Additionally, histological characterization of the adipose tissue was performed. The results obtained showed that IL-6 expression in adipose tissue biopsies derived from animals with EMS was enhanced while TNF-α levels of both groups were comparable. Compared to the obese ponies, EMS animals also had significantly elevated levels of serum IL-6 and TNF-α. Histological analysis revealed macrophage infiltration and fibrosis in adipose tissue preparations from the EMS group. These data suggest that IL-6 may play a key role in the course of EMS in Welsh ponies. Our findings also demonstrated that analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines levels in serum may serve as an additional tool for diagnosing EMS.
Keywords: equine metabolic syndrome; interleukin-6; leptin; subcutaneous adipose tissue; tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The influence of equine body weight gain on inflammatory cytokine expressions of adipose tissue in response to endotoxin challenge.Acta Vet Scand. 2020 Apr 22;62(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13028-020-00515-5. Acta Vet Scand. 2020. PMID: 32321549 Free PMC article.
-
Heritability of metabolic traits associated with equine metabolic syndrome in Welsh ponies and Morgan horses.Equine Vet J. 2019 Jul;51(4):475-480. doi: 10.1111/evj.13053. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Equine Vet J. 2019. PMID: 30472742
-
Effects of body weight reduction on blood adipokines and subcutaneous adipose tissue adipokine mRNA expression profiles in obese ponies.Vet Rec. 2012 Nov 24;171(21):528. doi: 10.1136/vr.100911. Epub 2012 Oct 7. Vet Rec. 2012. PMID: 23042851
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipose tissue.Proc Nutr Soc. 2001 Aug;60(3):349-56. doi: 10.1079/pns2001110. Proc Nutr Soc. 2001. PMID: 11681809 Review.
-
The equine metabolic syndrome peripheral Cushing's syndrome.Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2002 Aug;18(2):271-93. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0739(02)00006-8. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2002. PMID: 15635908 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Chronic Inflammation and Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Course of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Therapy.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Oct 22;2018:4274361. doi: 10.1155/2018/4274361. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30425746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Properties of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Treated with 5-Azacytydine and Resveratrol on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and Macrophages in Metabolic Syndrome Animals.J Clin Med. 2018 Oct 24;7(11):383. doi: 10.3390/jcm7110383. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30356025 Free PMC article.
-
Arthrospira platensis enriched with Cr(III), Mg(II), and Mn(II) ions improves insulin sensitivity and reduces systemic inflammation in equine metabolic affected horses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 16;15:1382844. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1382844. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38689728 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of equine body weight gain on inflammatory cytokine expressions of adipose tissue in response to endotoxin challenge.Acta Vet Scand. 2020 Apr 22;62(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13028-020-00515-5. Acta Vet Scand. 2020. PMID: 32321549 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Host Factors Associated with the Development of Equine Herpesvirus Myeloencephalopathy by Transcriptomic Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Horses.Viruses. 2021 Feb 24;13(3):356. doi: 10.3390/v13030356. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33668216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertin E, Nguyen P, Guenounou M, Durlach V, Potron G, Leutenegger M. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) are essentially dependent on visceral fat amount in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab J. 2000;26:178–182. - PubMed
-
- Carter RA, Geor RJ, Staniar WB, Cubitt TA, Harris PA. Apparent adiposity assessed by standardised scoring systems and morphometric measurements in horses and ponies. Vet J. 2009;179:204–210. - PubMed
-
- Dugdale AH, Curtis GC, Cripps P, Harris PA, Argo CM. Effect of dietary restriction on body condition, composition and welfare of overweight and obese pony mares. Equine Vet J. 2010;42:600–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

