Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain
- PMID: 25270052
- PMCID: PMC4406874
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24768
Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain
Abstract
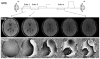
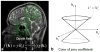
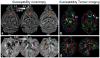
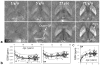
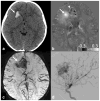
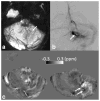
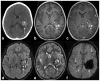
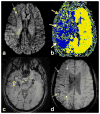
Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique that enhances image contrast by using the susceptibility differences between tissues. It is created by combining both magnitude and phase in the gradient echo data. SWI is sensitive to both paramagnetic and diamagnetic substances which generate different phase shift in MRI data. SWI images can be displayed as a minimum intensity projection that provides high resolution delineation of the cerebral venous architecture, a feature that is not available in other MRI techniques. As such, SWI has been widely applied to diagnose various venous abnormalities. SWI is especially sensitive to deoxygenated blood and intracranial mineral deposition and, for that reason, has been applied to image various pathologies including intracranial hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, stroke, neoplasm, and multiple sclerosis. SWI, however, does not provide quantitative measures of magnetic susceptibility. This limitation is currently being addressed with the development of quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) and susceptibility tensor imaging (STI). While QSM treats susceptibility as isotropic, STI treats susceptibility as generally anisotropic characterized by a tensor quantity. This article reviews the basic principles of SWI, its clinical and research applications, the mechanisms governing brain susceptibility properties, and its practical implementation, with a focus on brain imaging.
Keywords: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MSA, magnetic susceptibility anisotropy; QSM, quantitative susceptibility mapping; STI, susceptibility tensor imaging; SWI, susceptibility weighted imaging; TBI, traumatic brain injury; hemorrhage; iron; multiple sclerosis; myelin; stroke.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


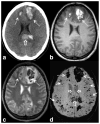
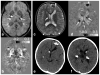
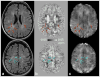
References
-
- Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR. Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Magn Reson Med. 2004;52:612–618. - PubMed
-
- de Crespigny AJ, Roberts TP, Kucharcyzk J, Moseley ME. Improved sensitivity to magnetic susceptibility contrast. Magn Reson Med. 1993;30:135–137. - PubMed
-
- Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke EM. Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology. 1997;204:272–277. - PubMed
-
- de Rochefort L, Brown R, Prince MR, Wang Y. Quantitative MR susceptibility mapping using piece-wise constant regularized inversion of the magnetic field. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60:1003–1009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

