Protein solubilization: a novel approach
- PMID: 25270058
- PMCID: PMC4254358
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.09.003
Protein solubilization: a novel approach
Abstract
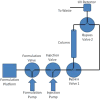
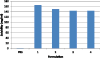
Formulation development presents significant challenges with respect to protein therapeutics. One component of these challenges is to attain high protein solubility (>50mg/ml for immunoglobulins) with minimal aggregation. Protein-protein interactions contribute to aggregation and the integral sum of these interactions can be quantified by a thermodynamic parameter known as the osmotic second virial coefficient (B-value). The method presented here utilizes high-throughput measurement of B-values to identify the influence of additives on protein-protein interactions. The experiment design uses three tiers of screens to arrive at final solution conditions that improve protein solubility. The first screen identifies individual additives that reduce protein interactions. A second set of B-values are then measured for different combinations of these additives via an incomplete factorial screen. Results from the incomplete factorial screen are used to train an artificial neural network (ANN). The "trained" ANN enables predictions of B-values for more than 4000 formulations that include additive combinations not previously experimentally measured. Validation steps are incorporated throughout the screening process to ensure that (1) the protein's thermal and aggregation stability characteristics are not reduced and (2) the artificial neural network predictive model is accurate. The ability of this approach to reduce aggregation and increase solubility is demonstrated using an IgG protein supplied by Minerva Biotechnologies, Inc.
Keywords: Design of experiments; High-throughput screening; Neural network; Physical stability; Protein solubility; Self-interaction chromatography.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Mississippi State University in accordance with its policy on conflict of interest in research.
Figures

References
-
- Arnum PV. Pharmaceutical Technology. 2013;37:38.
-
- Johnson IS. Science. 1983;219:632. - PubMed
-
- Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:21. - PubMed
-
- Shire SJ, Shahrokh Z, Liu J. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2004;93:1390. - PubMed
-
- Schellekens H. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2005;20:vi3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

