Improved assemblies using a source-agnostic pipeline for MetaGenomic Assembly by Merging (MeGAMerge) of contigs
- PMID: 25270300
- PMCID: PMC4180827
- DOI: 10.1038/srep06480
Improved assemblies using a source-agnostic pipeline for MetaGenomic Assembly by Merging (MeGAMerge) of contigs
Abstract
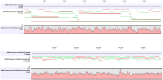
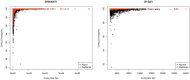
Assembly of metagenomic samples is a very complex process, with algorithms designed to address sequencing platform-specific issues, (read length, data volume, and/or community complexity), while also faced with genomes that differ greatly in nucleotide compositional biases and in abundance. To address these issues, we have developed a post-assembly process: MetaGenomic Assembly by Merging (MeGAMerge). We compare this process to the performance of several assemblers, using both real, and in-silico generated samples of different community composition and complexity. MeGAMerge consistently outperforms individual assembly methods, producing larger contigs with an increased number of predicted genes, without replication of data. MeGAMerge contigs are supported by read mapping and contig alignment data, when using synthetically-derived and real metagenomic data, as well as by gene prediction analyses and similarity searches. MeGAMerge is a flexible method that generates improved metagenome assemblies, with the ability to accommodate upcoming sequencing platforms, as well as present and future assembly algorithms.
Figures


References
-
- Scholz M. B. et al. Next generation sequencing and bioinformatic bottlenecks: the current state of metagenomic data analysis. Curr Opin Biotech 23, 9–15, 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.11.013 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Desai N. et al. From genomics to metagenomics. Curr Opin Biotech 23, 72–76, 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.12.017 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

