Collective antibiotic resistance: mechanisms and implications
- PMID: 25271119
- PMCID: PMC4367450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.09.003
Collective antibiotic resistance: mechanisms and implications
Abstract
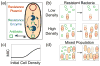
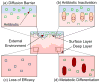
In collective resistance, microbial communities are able to survive antibiotic exposures that would be lethal to individual cells. In this review, we explore recent advances in understanding collective resistance in bacteria. The population dynamics of 'cheating' in a system with cooperative antibiotic inactivation have been described, providing insight into the demographic factors that determine resistance allele frequency in bacteria. Extensive work has elucidated mechanisms underlying collective resistance in biofilms and addressed questions about the role of cooperation in these structures. Additionally, recent investigations of 'bet-hedging' strategies in bacteria have explored the contributions of stochasticity and regulation to bacterial phenotypic heterogeneity and examined the effects of these strategies on community survival.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hogan D, Kolter R. Why are bacteria refractory to antimicrobials? Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002;5:472–477. - PubMed
-
- Yurtsev EA, Chao HX, Datta MS, Artemova T, Gore J. Bacterial cheating drives the population dynamics of cooperative antibiotic resistance plasmids. Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9 doi: 10.1038/msb.2013.39. Using a combination of experiments and modeling, this paper explores the population dynamics between resistant and sensitive bacteria growing in a medium containing the β-lactam antibiotic ampicillin. The paper shows that in the presence of resistant cells, sensitive cells can survive high antibiotic concentrations. The authors provide a simple model that successfully explains the observed dynamics, providing intuition for how inactivation of the antibiotic by resistant cells can result in coexistence between resistant and sensitive cells. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

