Ibrutinib treatment ameliorates murine chronic graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 25271622
- PMCID: PMC4347242
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI75328
Ibrutinib treatment ameliorates murine chronic graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
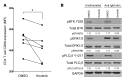
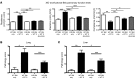
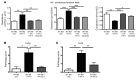
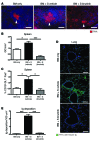
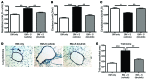
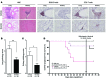
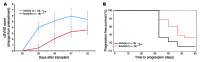
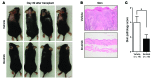
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) is a life-threatening impediment to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and current therapies do not completely prevent and/or treat cGVHD. CD4+ T cells and B cells mediate cGVHD; therefore, targeting these populations may inhibit cGVHD pathogenesis. Ibrutinib is an FDA-approved irreversible inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) and IL-2 inducible T cell kinase (ITK) that targets Th2 cells and B cells and produces durable remissions in B cell malignancies with minimal toxicity. Here, we evaluated whether ibrutinib could reverse established cGVHD in 2 complementary murine models, a model interrogating T cell-driven sclerodermatous cGVHD and an alloantibody-driven multiorgan system cGVHD model that induces bronchiolar obliterans (BO). In the T cell-mediated sclerodermatous cGVHD model, ibrutinib treatment delayed progression, improved survival, and ameliorated clinical and pathological manifestations. In the alloantibody-driven cGVHD model, ibrutinib treatment restored pulmonary function and reduced germinal center reactions and tissue immunoglobulin deposition. Animals lacking BTK and ITK did not develop cGVHD, indicating that these molecules are critical to cGVHD development. Furthermore, ibrutinib treatment reduced activation of T and B cells from patients with active cGVHD. Our data demonstrate that B cells and T cells drive cGVHD and suggest that ibrutinib has potential as a therapeutic agent, warranting consideration for cGVHD clinical trials.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA140158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA133250-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL56067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI034495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA183560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA133250/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA183559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009338-33-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL115761/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI34495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA095426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI1007313/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA142106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

