Acute increase of α-synuclein inhibits synaptic vesicle recycling evoked during intense stimulation
- PMID: 25273557
- PMCID: PMC4244201
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-02-0708
Acute increase of α-synuclein inhibits synaptic vesicle recycling evoked during intense stimulation
Abstract
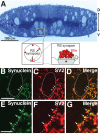
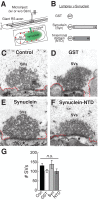
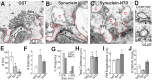
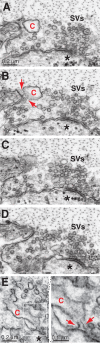
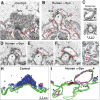
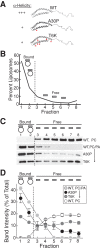
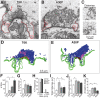
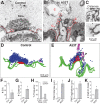
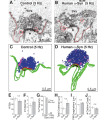
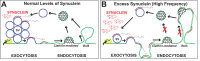
Parkinson's disease is associated with multiplication of the α-synuclein gene and abnormal accumulation of the protein. In animal models, α-synuclein overexpression broadly impairs synaptic vesicle trafficking. However, the exact steps of the vesicle trafficking pathway affected by excess α-synuclein and the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unknown. Therefore we acutely increased synuclein levels at a vertebrate synapse and performed a detailed ultrastructural analysis of the effects on presynaptic membranes. At stimulated synapses (20 Hz), excess synuclein caused a loss of synaptic vesicles and an expansion of the plasma membrane, indicating an impairment of vesicle recycling. The N-terminal domain (NTD) of synuclein, which folds into an α-helix, was sufficient to reproduce these effects. In contrast, α-synuclein mutants with a disrupted N-terminal α-helix (T6K and A30P) had little effect under identical conditions. Further supporting this model, another α-synuclein mutant (A53T) with a properly folded NTD phenocopied the synaptic vesicle recycling defects observed with wild type. Interestingly, the vesicle recycling defects were not observed when the stimulation frequency was reduced (5 Hz). Thus excess α-synuclein impairs synaptic vesicle recycling evoked during intense stimulation via a mechanism that requires a properly folded N-terminal α-helix.
© 2014 Busch et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures

References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, et al. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Boassa D, Berlanga ML, Yang MA, Terada M, Hu J, Bushong EA, Hwang M, Masliah E, George JM, Ellisman MH. Mapping the subcellular distribution of alpha-synuclein in neurons using genetically encoded probes for correlated light and electron microscopy: implications for Parkinson's disease pathogenesis. J Neurosci. 2013;33:2605–2615. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolte S, Cordelieres FP. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J Microsc. 2006;224:213–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

