Activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritis via lysophosphatidic acid-lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 cascade
- PMID: 25273676
- PMCID: PMC4203966
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-014-0461-9
Activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritis via lysophosphatidic acid-lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 cascade
Abstract
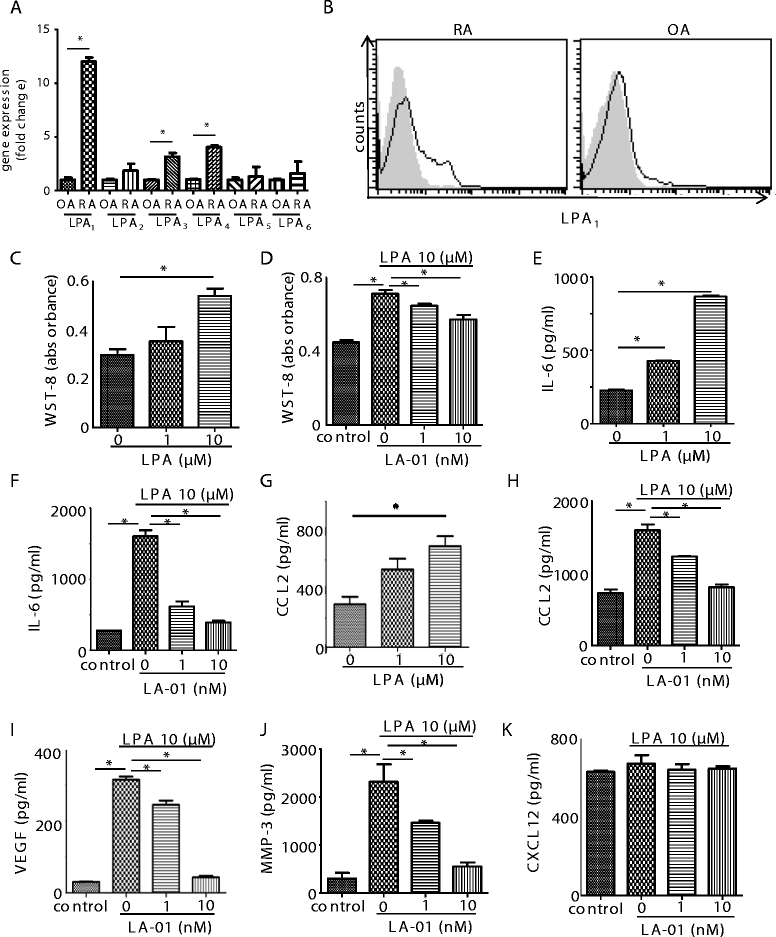
Introduction: Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a bioactive lipid that binds to G protein-coupled receptors (LPA1-6). Recently, we reported that abrogation of LPA receptor 1 (LPA1) ameliorated murine collagen-induced arthritis, probably via inhibition of inflammatory cell migration, Th17 differentiation and osteoclastogenesis. In this study, we examined the importance of the LPA-LPA1 axis in cell proliferation, cytokine/chemokine production and lymphocyte transmigration in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) obtained from the synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
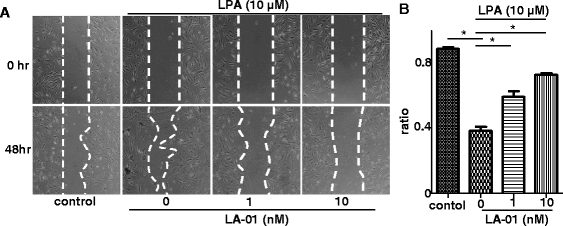
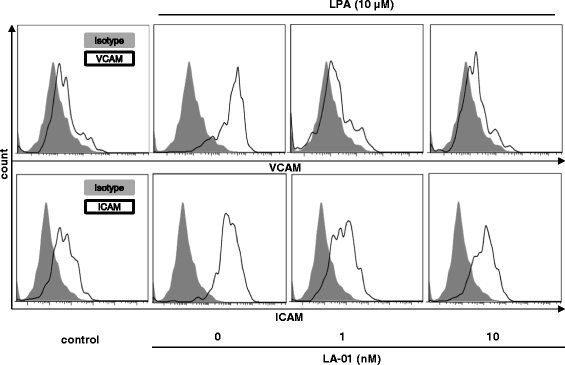
Methods: FLSs were prepared from synovial tissues of RA patients. Expression of LPA1-6 was examined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Cell surface LPA1 expression was analyzed by flow cytometry. Cell proliferation was analyzed using a cell-counting kit. Production of interleukin 6 (IL-6), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), metalloproteinase 3 (MMP-3) and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (CXCL12) was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Pseudoemperipolesis was evaluated using a coculture of RA FLSs and T or B cells. Cell motility was examined by scrape motility assay. Expression of adhesion molecules was determined by flow cytometry.
Results: The expression of LPA1 mRNA and cell surface LPA1 was higher in RA FLSs than in FLSs from osteoarthritis tissue. Stimulation with LPA enhanced the proliferation of RA FLSs and the production of IL-6, VEGF, CCL2 and MMP-3 by FLSs, which were suppressed by an LPA1 inhibitor (LA-01). Ki16425, another LPA1 antagonist, also suppressed IL-6 production by LPA-stimulated RA FLSs. However, the production of CXCL12 was not altered by stimulation with LPA. LPA induced the pseudoemperipolesis of T and B cells cocultured with RA FLSs, which was suppressed by LPA1 inhibition. In addition, LPA enhanced the migration of RA FLSs and expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule and intercellular adhesion molecule on RA FLSs, which were also inhibited by an LPA1 antagonist.
Conclusions: Collectively, these results indicate that LPA-LPA1 signaling contributes to the activation of RA FLSs.
Figures

References
-
- Kawagoe H, Stracke ML, Nakamura H, Sano K. Expression and transcriptional regulation of the PD-Iα/autotaxin gene in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2516–2521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

