Pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy
- PMID: 25274301
- PMCID: PMC4236859
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13807
Pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy
Abstract
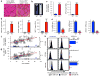
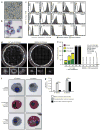
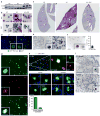
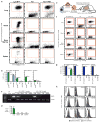
Bone-marrow transplantation is an effective cell therapy but requires myeloablation, which increases infection risk and mortality. Recent lineage-tracing studies documenting that resident macrophage populations self-maintain independently of haematological progenitors prompted us to consider organ-targeted, cell-specific therapy. Here, using granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) receptor-β-deficient (Csf2rb(-/-)) mice that develop a myeloid cell disorder identical to hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (hPAP) in children with CSF2RA or CSF2RB mutations, we show that pulmonary macrophage transplantation (PMT) of either wild-type or Csf2rb-gene-corrected macrophages without myeloablation was safe and well-tolerated and that one administration corrected the lung disease, secondary systemic manifestations and normalized disease-related biomarkers, and prevented disease-specific mortality. PMT-derived alveolar macrophages persisted for at least one year as did therapeutic effects. Our findings identify mechanisms regulating alveolar macrophage population size in health and disease, indicate that GM-CSF is required for phenotypic determination of alveolar macrophages, and support translation of PMT as the first specific therapy for children with hPAP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

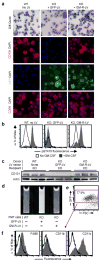

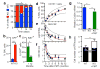

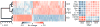
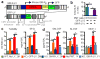
Comment in
-
Lung disease: Treatment by cell transplant.Nature. 2014 Oct 23;514(7523):438-40. doi: 10.1038/nature13758. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25274303 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tanaka T, et al. Adult-onset hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by a single-base deletion in CSF2RB. J Med Genet. 2011;48:205–209. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, et al. Hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by recessive CSF2RB mutations. The European respiratory journal. 2011;37:201–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 HL069549/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 8UL1TR000077-05/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL118342/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR-47363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK078392/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118342/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL127672/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK90971/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL085453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK78392/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR047363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000077/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK090971/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL106134/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

