T cell immune abnormalities in immune thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 25274611
- PMCID: PMC4189678
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-014-0072-6
T cell immune abnormalities in immune thrombocytopenia
Abstract
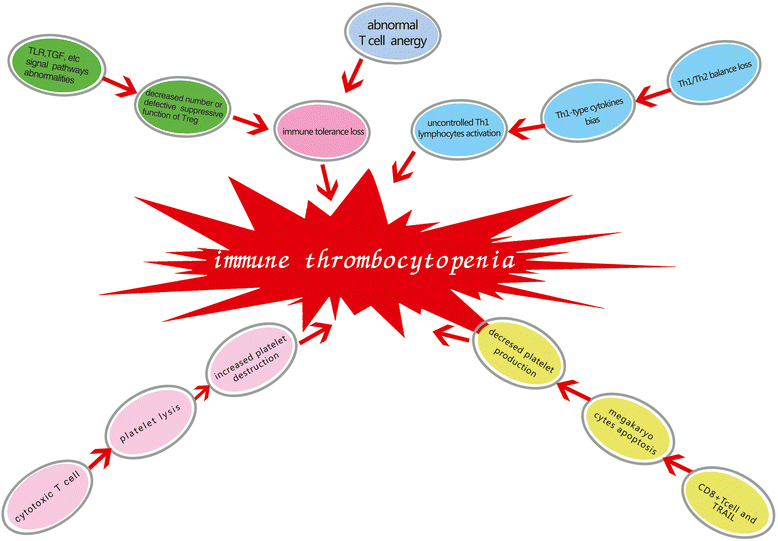
Immune thrombocytopenia is an autoimmune disease with abnormal T cell immunity. Cytotoxic T cells, abnormal T regulatory cells, helper T cell imbalance, megakaryocyte maturation abnormalities and abnormal T cell anergy are involved in the pathogenesis of this condition. The loss of T cell-mediated immune tolerance to platelet auto-antigens plays a crucial role in immune thrombocytopenia. The induction of T cell tolerance is an important mechanism by which the pathogenesis and treatment of immune thrombocytopenia can be studied. Studies regarding the roles of the new inducible costimulator signal transduction pathway, the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, and the nuclear factor kappa B signal transduction pathway in the induction of T cell tolerance can help improve our understanding of immune theory and may provide a new theoretical basis for studying the pathogenesis and treatment of immune thrombocytopenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 in immune thrombocytopenia.Scand J Immunol. 2014 Apr;79(4):231-6. doi: 10.1111/sji.12153. Scand J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24383985 Review.
-
Biomarkers for immune thrombocytopenia.Biomark Res. 2015 Jul 16;3:19. doi: 10.1186/s40364-015-0045-0. eCollection 2015. Biomark Res. 2015. PMID: 26185681 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of regulatory T cells in gene transfer.Curr Gene Ther. 2007 Oct;7(5):381-90. doi: 10.2174/156652307782151506. Curr Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17979684 Review.
-
Phagocytosis of platelets by Kupffer cells in immune thrombocytopenia.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Jun;111(6):563-5. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987. PMID: 3579514
-
Neonatal tolerance to a Th2-mediated autoimmune disease generates CD8+ Tc1 regulatory cells.J Autoimmun. 2003 Nov;21(3):201-12. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(03)00118-5. J Autoimmun. 2003. PMID: 14599845
Cited by
-
Molecular alterations in the TCR signaling pathway in patients with aplastic anemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Mar 31;9:32. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0261-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27036622 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating level of Th17 cells is associated with sensitivity to glucocorticoids in patients with immune thrombocytopenia.Int J Hematol. 2018 Apr;107(4):442-450. doi: 10.1007/s12185-017-2392-0. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Int J Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29327325
-
Upregulation of necroptosis markers RIPK3/MLKL and their crosstalk with autophagy-related protein Beclin-1 in primary immune thrombocytopenia.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jun;23(2):447-456. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00839-8. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 35699825 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge mapping of immune thrombocytopenia: a bibliometric study.Front Immunol. 2023 May 3;14:1160048. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1160048. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37207211 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Review of Pathogenesis and Treatment Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 10;25(4):2163. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042163. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olsson B, Andersson PO, Jacobsson S, Carlsson L, Wadenvik A. Disturbed apoptosis of T-cells in patients with active idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:139–144. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XL, Peng J, Sun JZ, Guo CS, Yu Y, Wang ZG, Chu XX, Hou M. Modulation of immune response with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 immunoglobulin-induced anergic T cells in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:158–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02804.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang XL, Peng J, Sun JZ, Liu JJ, Guo CS, Wang ZG, Yu Y, Shi Y, Qin P, Li SG, Zhang LN, Hou M. De novo induction of platelet-specific CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells from CD4(+) CD25(−) cells in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2009;113:2568–2577. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-148288. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aslam R, Hu Y, Gebremeskel S, Segel GB, Speck ER, Guo L, Kim M, Ni H, Freedman J, Semple JW. Thymic retention of CD4 + CD25 + FoxP3+ T regulatory cells is associated with their peripheral deficiency and thrombocytopenia in a murine model of immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2012;120:2127–2132. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-413526. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

