LEADER 3--lipase and amylase activity in subjects with type 2 diabetes: baseline data from over 9000 subjects in the LEADER Trial
- PMID: 25275271
- PMCID: PMC4206347
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000229
LEADER 3--lipase and amylase activity in subjects with type 2 diabetes: baseline data from over 9000 subjects in the LEADER Trial
Abstract
Objectives: This report from the LEADER (Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results) trial describes baseline lipase and amylase activity in type 2 diabetic subjects without acute pancreatitis symptoms before randomization to the glucagonlike peptide analog liraglutide or placebo.
Methods: The LEADER is an international randomized placebo-controlled trial evaluating the cardiovascular safety of liraglutide in 9340 type 2 diabetic patients at high cardiovascular risk. Fasting lipase and amylase activity was assessed at baseline, before receiving liraglutide or placebo, using a commercial assay (Roche) with upper limit of normal values of 63 U/L for lipase and 100 U/L for amylase.
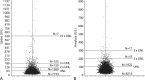
Results: Either or both enzymes were above the upper limit of normal in 22.7% of subjects; 16.6% (n = 1540) had an elevated lipase level (including 1.2% >3-fold elevated), and 11.8% (n = 1094) had an elevated amylase level (including 0.2% >3-fold elevated). In multivariable regression models, severely reduced kidney function was associated with the largest effect on increasing activity of both. However, even among subjects with normal kidney function, 12.2% and 7.7% had elevated lipase and amylase levels.
Conclusions: In this large study of type 2 diabetic patients, nearly 25% had elevated lipase or amylase levels without symptoms of acute pancreatitis. The clinician must take these data into account when evaluating abdominal symptoms in type 2 diabetic patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01179048.
Figures
References
-
- Girman CJ, Kou TD, Cai B, et al. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have higher risk for acute pancreatitis compared with those without diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010; 12: 766– 771 - PubMed
-
- Denker PS, Dimarco PE. Exenatide (exendin-4)-induced pancreatitis: a case report. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29: 471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical