Manufacturing and characterization of a recombinant adeno-associated virus type 8 reference standard material
- PMID: 25275822
- PMCID: PMC4236062
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2014.057
Manufacturing and characterization of a recombinant adeno-associated virus type 8 reference standard material
Abstract
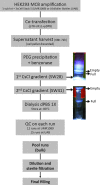
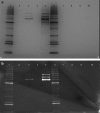
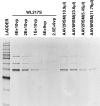
Abstract Gene therapy approaches using recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (rAAV2) and serotype 8 (rAAV8) have achieved significant clinical benefits. The generation of rAAV Reference Standard Materials (RSM) is key to providing points of reference for particle titer, vector genome titer, and infectious titer for gene transfer vectors. Following the example of the rAAV2RSM, here we have generated and characterized a novel RSM based on rAAV serotype 8. The rAAV8RSM was produced using transient transfection, and the purification was based on density gradient ultracentrifugation. The rAAV8RSM was distributed for characterization along with standard assay protocols to 16 laboratories worldwide. Mean titers and 95% confidence intervals were determined for capsid particles (mean, 5.50×10(11) pt/ml; CI, 4.26×10(11) to 6.75×10(11) pt/ml), vector genomes (mean, 5.75×10(11) vg/ml; CI, 3.05×10(11) to 1.09×10(12) vg/ml), and infectious units (mean, 1.26×10(9) IU/ml; CI, 6.46×10(8) to 2.51×10(9) IU/ml). Notably, there was a significant degree of variation between institutions for each assay despite the relatively tight correlation of assay results within an institution. This outcome emphasizes the need to use RSMs to calibrate the titers of rAAV vectors in preclinical and clinical studies at a time when the field is maturing rapidly. The rAAV8RSM has been deposited at the American Type Culture Collection (VR-1816) and is available to the scientific community.
Figures
References
-
- ATCC Virus Reference Materials. Available at: www.lgcstandards-atcc.org/Standards/Standards_Programs/ATCC_Virus_Refere... (accessed Oct. 24, 2014)
-
- Ayuso E., Mingozzi F., Montane J., et al. (2010). High AAV vector purity results in serotype- and tissue-independent enhancement of transduction efficiency. Gene Ther. 17, 503–510 - PubMed
-
- Ayuso E., Blouin V., Darmon C., et al. (2012). Reference materials for the characterization of adeno-associated viral vectors. In The Clinibook: Clinical Gene Transfer State of the Art. Cohen-haguenauer O., ed. (EDK, Paris: ) pp.83–90
-
- Bainbridge J.W., Smith A.J., Barker S.S., et al. (2008). Effect of gene therapy on visual function in Leber's congenital amaurosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 2231–2239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

