Antihyperlipidemic potential of Albizia amara (Roxb) Boiv. bark against Triton X-100 induced hyperlipidemic condition in rats
- PMID: 25276061
- PMCID: PMC4166812
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-8490.138237
Antihyperlipidemic potential of Albizia amara (Roxb) Boiv. bark against Triton X-100 induced hyperlipidemic condition in rats
Abstract
Background: The plant Albizia amara (Roxb.) Boiv. bark was used in traditional medical practices of India to treat cardiovascular diseases. Hyperlipidemia is the greatest risk factor of coronary heart disease.
Objective: The objective of this study was to screen the potential of A. amara against the condition of hyperlipidemia in rats.
Materials and methods: The antihyperlipidemic activity of A. amara ethanolic extract (AAEE) was studied on Triton X-100 induced model of hyperlipidemia in rats. Hyperlipidemia in experimental rats was evidenced by an enhancement in the levels of serum cholesterol, triglycerides (TGs), low density lipoprotein (LDL), very LDL (VLDL) and decrease in high density lipoprotein (HDL).
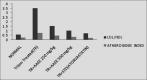
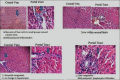
Results: AAEE showed significant antihyperlipidemic effect by lowering the serum levels of biochemical parameters such as a significant reduction in the level of serum cholesterol, TG (104.1 ± 3.39), LDL (48.2 ± 2.19), VLDL (20.81 ± 0.67) and increase in HDL (47.25 ± 2.05) level with an increase in a dose of AAEE (41.39 ± 1.24) < (47.25 ± 2.05), which was similar to the standard drug atorvastatin. The results of serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase and serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase also revealed that the plant extract was found to be safe on liver. Histopathological evaluation also revealed the positive effect of the plant extract. Preliminary phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of phytoconstituents such as saponins, glycosides and tannins. The preliminary chemical constituents stood as a strong evidence for the study.
Conclusion: Summing up the evidences of the pragmatic study, we can conclude that the extract of A. amara (Roxb.) Boiv. Bark aids in declining the condition of hyperlipidemia in rats.
Keywords: Albizia amara; Triton X-100; atorvastatin; hyperlipidemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
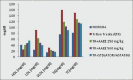

References
-
- Dhuley J, Naik SR, Rele S, Banerji A. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant activity of diallyl disulphide in rats. Pharm Pharmacol Commun. 1999;5:689.
-
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–421. - PubMed
-
- Dhulasavant V, Shinde S, Pawar M, Naikwade NS. Antihyperlipidemic activity of Cinnamomum tamala Nees. on high cholesterol diet induced. Int J PharmTech Res. 2010;2:2517–21.
-
- Sharma N, Garg V. Antidiabetic and antioxidant potential of ethanolic extract of Butea monosperma leaves in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2009;46:99–105. - PubMed
-
- Mitra Mazumder P, Sasmal D, Ghosh AR, Paramaguru R. Evaluation of antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activity of Pterospermum acerifolium (L) willd. Pharmacologyonline. 2011;3:128–46.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
