Amyloidosis of the head and neck: a clinicopathological study of cases with long-term follow-up
- PMID: 25276173
- PMCID: PMC4175762
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2013.39206
Amyloidosis of the head and neck: a clinicopathological study of cases with long-term follow-up
Figures
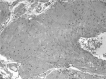
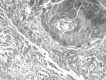


References
-
- von Rokitansky KF. Handbuch der pathologischen Anatomie. Vienna: Braumuller&Seidel; 1842. pp. 209–49.
-
- Virchow R. Bav and Zussmmersetzying der Corporci Amalacca des Menschen. Vehr Phys Med Geswurzlurg. 1851;2:51–3.
-
- Westermark P. Aspects on human amyloid forms and their fibril polypeptides. FEBS J. 2005;272:5942–9. - PubMed
-
- Alaani A, Warfield AT, Pracy JP. Management of laryngeal amyloidosis. J Laryngol Otol. 2004;118:279–83. - PubMed
-
- Pepys MB, Herbert J, Hutchinson WL, et al. Targeted pharmacological depletion of serum amyloid P component for treatment of human amyloidosis. Nature. 2002;417:254–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
