The quality-coverage gap in antenatal care: toward better measurement of effective coverage
- PMID: 25276575
- PMCID: PMC4168625
- DOI: 10.9745/GHSP-D-13-00176
The quality-coverage gap in antenatal care: toward better measurement of effective coverage
Abstract
Background: The proportion of pregnant women receiving 4 or more antenatal care visits (ANC 4+) is used prominently as a global benchmark indicator to track maternal health program performance. This has contributed to an inappropriate focus on the number of contacts rather than on the content and process of care. This paper presents analysis of specific elements of care received among women reporting 4 or more ANC visits.
Methods: We conducted secondary analysis using Demographic and Health Survey data from 41 countries to determine coverage for specific elements of antenatal care. The analysis was conducted for: (1) women who delivered during the 2 years preceding the survey and who reported receiving 4 or more ANC visits, and (2) all women who delivered during the preceding 2 years. The specific ANC services that we assessed were: blood pressure measurement, tetanus toxoid vaccination, first ANC visit at less than 4 months gestation, urine testing, counseling about danger signs, HIV counseling and testing, iron-folate supplementation (≥ 90 days), and at least 2 doses of sulfadoxine/pyramethamine for malaria prevention. The difference between expected (100%) and actual coverage (the quality-coverage gap) was calculated for each service across the 41 surveys.
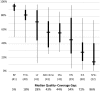
Results: Coverage for specific elements of care among women reporting 4 or more ANC visits was generally low for most of the specific elements assessed. Blood pressure and tetanus toxoid performed best, with median quality-coverage gaps of 5% and 18%, respectively. The greatest gaps were for iron-folate supplementation (72%) and malaria prevention (86%). Coverage for specific interventions was generally much lower among all pregnant women (reflecting population effective coverage) than among only those who had received ANC 4+ visits. Although ANC 4+ and average coverage across the elements of care correlated relatively well (Pearson r(2) = 0.56), most countries had lower average coverage for the content of care than for ANC 4+ (among all pregnant women).
Conclusion: We argue for the adoption of a summary indicator that better reflects the content of antenatal care than does the current ANC 4+ indicator. We propose, as an alternative, the simple average of a set of ANC content indicators available through surveys and routine health information systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Indicators for Monitoring the Millennium Development Goals: Definitions, Rationale, Concepts and Sources [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 2012 Nov 19. 5.5 Antenatal care coverage (at least one visit and at least four visits); 2012 Mar 5 [cited 2013 Jul 1]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mi/wiki/5-5-Antenatal-care-coverage-at-least-one...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), Commission on Information and Accountability for Women's and Children's Health. Keeping promises, measuring results. Geneva: WHO; 2011. Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/millennium_development_goals/accountability_co...
-
- Villar J, Ba'aqeel H, Piaggio G, Lumbiganon P, Miguel Belizán J, Farnot U, et al. ; WHO Antenatal Care Trial Research Group. WHO antenatal care randomised trial for the evaluation of a new model of routine antenatal care. Lancet. 2001;357(9268): 1551–1564 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04722-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhutta ZA, Darmstadt GL, Hasan BS, Haws RA. Community-based interventions for improving perinatal and neonatal health outcomes in developing countries: a review of the evidence. Pediatrics. 2005;115(2 Suppl): 519–617 - PubMed
-
- Rutstein SO, Rojas G. Guide to DHS statistics: demographic and health surveys methodology. Calverton (MD): ORC Macro; 2006. Available from: http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/DHSG1/Guide_to_DHS_Statistics_29Oct2012_D...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
