The modified mid-anterior portal for hip arthroscopy
- PMID: 25276606
- PMCID: PMC4175545
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2014.05.005
The modified mid-anterior portal for hip arthroscopy
Abstract
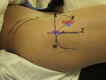
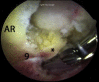
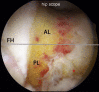
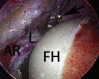
The modified mid-anterior portal is a utilitarian hip arthroscopy working portal that permits dual-portal comprehensive surgery for femoroacetabular impingement and related chondrolabral procedures without the need for interportal exchange. Its distal location facilitates labral reparative and reconstructive procedures while minimizing iatrogenic acetabular chondral damage. The relatively lateral location permits instrument navigation not only along the anterosuperior acetabular rim and anterolateral proximal femur typically required for acetabuloplasty and femoroplasty but even to the posterior regions of the hip in cases of global pincer femoroacetabular impingement and posterior extensions of cam morphology and the anteromedial proximal femur while avoiding direct injury to the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.
Figures


References
-
- Safran M.R. Advances in hip arthroscopy. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2010;18:55. - PubMed
-
- Larson CM. Complications after hip arthroscopy: A prospective, multicenter, study using a validated grading classification. Presented at the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, July 11-14, 2013.
-
- Freehill M.T., Safran M.R. The labrum of the hip: Diagnosis and rationale for surgical correction. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30:293–315. - PubMed
-
- Robertson W.J., Kelly B.T. The safe zone for hip arthroscopy: A cadaveric assessment of central, peripheral, and lateral compartment portal placement. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:1019–1026. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

