Effects of the combined PDL/Nd:YAG laser on surgical scars: vascularity and collagen changes evaluated by in vivo confocal microscopy
- PMID: 25276770
- PMCID: PMC4174963
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/204532
Effects of the combined PDL/Nd:YAG laser on surgical scars: vascularity and collagen changes evaluated by in vivo confocal microscopy
Abstract
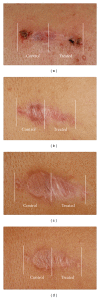
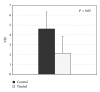
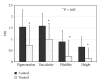
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of the sequential combined 585 nm PDL and the 1064 nm neodymium:yttrium-aluminium-garnet laser (PDL/Nd:YAG) in the treatment of surgical scars and to evaluate the short-term effects by in vivo confocal microscopy (RCM) and the long-term effects by clinical assessment of the scars. Twenty-five patients were enrolled with 39 postoperative linear scars; each scar was divided into two fields. One half was treated with the combined PDL/Nd:YAG laser, whereas the other half remained untreated. Each scar was treated three times at monthly intervals. Scars were evaluated by an independent examiner, using the Vancouver Scar Scale. The combined PDL/Nd:YAG laser significantly improved the appearance of the scars. In order to study the short-term effects of combined laser treatment, six additional patients were enrolled with 7 postoperative linear scars. One half of scars was treated once with the combined PDL/Nd:YAG laser. One week after this laser treatment, both the treated and the nontreated parts of the scars were examined by dermoscopy and RCM. The dermoscopic pictures revealed improvements even in treated areas. In conclusion, the combined PDL/Nd:YAG laser was found to be effective in improving the quality and appearance of the surgical scars.
Figures


References
-
- Tziotzios C, Profyris C, Sterling J. Cutaneous scarring: pathophysiology, molecular mechanisms, and scar reduction therapeutics: part II. Strategies to reduce scar formation after dermatologic procedures. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2012;66(1):13–24. - PubMed
-
- Eming SA, Krieg T, Davidson JM. Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2007;127(3):514–525. - PubMed
-
- Gold MH. Dermabrasion in dermatology. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2003;4(7):467–471. - PubMed
-
- Musgrave MA, Umraw N, Fish JS, Gomez M, Cartotto RC. The effect of silicone gel sheets on perfusion of hypertrophic burn scars. Journal of Burn Care & Rehabilitation. 2002;23(3):208–214. - PubMed
-
- Bouzari N, Davis SC, Nouri K. Laser treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. International Journal of Dermatology. 2007;46(1):80–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

