The brain correlates of the effects of monetary and verbal rewards on intrinsic motivation
- PMID: 25278834
- PMCID: PMC4166960
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00303
The brain correlates of the effects of monetary and verbal rewards on intrinsic motivation
Abstract
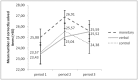
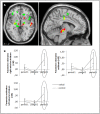
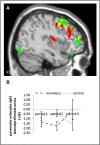
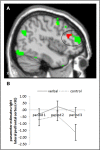
Apart from everyday duties, such as doing the laundry or cleaning the house, there are tasks we do for pleasure and enjoyment. We do such tasks, like solving crossword puzzles or reading novels, without any external pressure or force; instead, we are intrinsically motivated: we do the tasks because we enjoy doing them. Previous studies suggest that external rewards, i.e., rewards from the outside, affect the intrinsic motivation to engage in a task: while performance-based monetary rewards are perceived as controlling and induce a business-contract framing, verbal rewards praising one's competence can enhance the perceived self-determination. Accordingly, the former have been shown to decrease intrinsic motivation, whereas the latter have been shown to increase intrinsic motivation. The present study investigated the neural processes underlying the effects of monetary and verbal rewards on intrinsic motivation in a group of 64 subjects applying functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). We found that, when participants received positive performance feedback, activation in the anterior striatum and midbrain was affected by the nature of the reward; compared to a non-rewarded control group, activation was higher while monetary rewards were administered. However, we did not find a decrease in activation after reward withdrawal. In contrast, we found an increase in activation for verbal rewards: after verbal rewards had been withdrawn, participants showed a higher activation in the aforementioned brain areas when they received success compared to failure feedback. We further found that, while participants worked on the task, activation in the lateral prefrontal cortex was enhanced after the verbal rewards were administered and withdrawn.
Keywords: crowding-out; fMRI; intrinsic motivation; monetary rewards; verbal rewards.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The rewarding value of good motor performance in the context of monetary incentives.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Jul;50(8):1739-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.03.030. Epub 2012 May 6. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22569215
-
Identifying the neural substrates of intrinsic motivation during task performance.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2017 Oct;17(5):939-953. doi: 10.3758/s13415-017-0524-x. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28639132
-
The Bright and Dark Sides of Performance-Dependent Monetary Rewards: Evidence From Visual Perception Tasks.Cogn Sci. 2020 Mar;44(3):e12825. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12825. Cogn Sci. 2020. PMID: 32180260
-
Effects of alexithymia and empathy on the neural processing of social and monetary rewards.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Jul;222(5):2235-2250. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1339-1. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 27866269
-
Applying self-determination theory to understand the motivational impact of cash rewards: New evidence from lab experiments.Int J Psychol. 2020 Jun;55(3):487-498. doi: 10.1002/ijop.12612. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Int J Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31385612 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Insights in motivation and reward - 2022.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Oct 18;17:1290548. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1290548. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37920805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Desire for Success Awakens: Proof of Competence Restoration in a Non-competitive Environment.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 21;15:698777. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.698777. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34234644 Free PMC article.
-
Man's Pursuit of Meaning: Unexpected Termination Bolsters One's Autonomous Motivation in an Irrelevant Ensuing Activity.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Mar 27;14:81. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00081. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32317948 Free PMC article.
-
A Multidimensional View on Social and Non-Social Rewards.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Aug 19;11:818. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00818. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32973574 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Verbal Rewards, Creative Self-Efficacy, and Creative Behavior: A Perspective of Cognitive Appraisal Theory.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;13(3):229. doi: 10.3390/bs13030229. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36975255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camerer C., Hogarth R. (1999). The effects of financial incentives in experiments: a review and capital-labor-production framework. J. Risk Uncertain. 19, 7–42 10.1023/A:1007850605129 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

