Stroke, multimorbidity and polypharmacy in a nationally representative sample of 1,424,378 patients in Scotland: implications for treatment burden
- PMID: 25280748
- PMCID: PMC4220053
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-014-0151-0
Stroke, multimorbidity and polypharmacy in a nationally representative sample of 1,424,378 patients in Scotland: implications for treatment burden
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of multimorbidity (the presence of two or more long-term conditions) is rising internationally. Multimorbidity affects patients by increasing their burden of symptoms, but is also likely to increase the self-care demands, or treatment burden, that they experience. Treatment burden refers to the effort expended in operationalising treatments, navigating healthcare systems and managing relations with healthcare providers. This is an important problem for people with chronic illness such as stroke. Polypharmacy is an important marker of both multimorbidity and burden of treatment. In this study, we examined the prevalence of multimorbidity and polypharmacy in a large, nationally representative population of primary care patients with and without stroke, adjusting for age, sex and deprivation.
Methods: A cross-sectional study of 1,424,378 participants aged 18 years and over, from 314 primary care practices in Scotland that were known to be demographically representative of the Scottish adult population. Data included information on the presence of stroke and another 39 long-term conditions, plus prescriptions for regular medications.
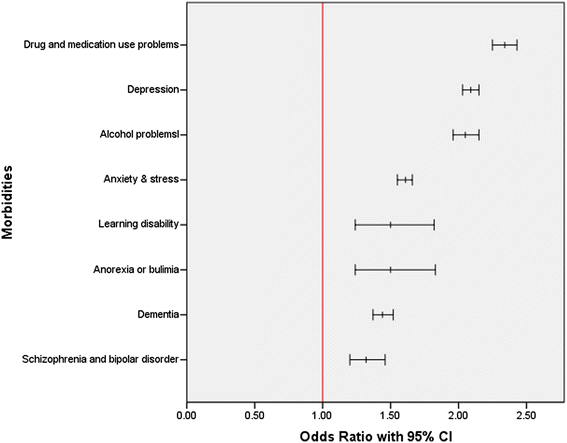
Results: In total, 35,690 people (2.5%) had a diagnosis of stroke. Of the 39 comorbidities examined, 35 were significantly more common in people with stroke. Of the people with a stroke, the proportion that had one or more additional morbidities present (94.2%) was almost twice that in the control group (48%) (odds ratio (OR) adjusted for age, sex and socioeconomic deprivation 5.18; 95% confidence interval (CI) 4.95 to 5.43). In the stroke group, 12.6% had a record of 11 or more repeat prescriptions compared with only 1.5% of the control group (OR adjusted for age, sex, deprivation and morbidity count 15.84; 95% CI 14.86 to 16.88). Limitations include the use of data collected for clinical rather than research purposes, a lack of consensus in the literature on the definition of certain long-term conditions, and the absence of statistical weighting in the measurement of multimorbidity, although the latter was deemed suitable for descriptive analyses.
Conclusions: Multimorbidity and polypharmacy were strikingly more common in those with a diagnosis of stroke compared with those without. This has important implications for clinical guidelines and the design of health services.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

