Effect of status epilepticus and antiepileptic drugs on CYP2E1 brain expression
- PMID: 25280786
- PMCID: PMC4383726
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.09.055
Effect of status epilepticus and antiepileptic drugs on CYP2E1 brain expression
Abstract
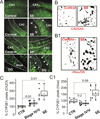
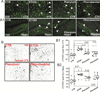
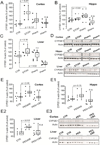
P450 metabolic enzymes are expressed in the human and rodent brain. Recent data support their involvement in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. However, the determinants of metabolic enzyme expression in the epileptic brain are unclear. We tested the hypothesis that status epilepticus (SE) or exposure to phenytoin or phenobarbital affects brain expression of the metabolic enzyme CYP2E1. SE was induced in C57BL/6J mice by systemic kainic acid. Brain CYP2E1 expression was evaluated 18-24h after severe SE by immunohistochemistry. Co-localization with neuronal nuclei (NEUN), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and CD31 was determined by confocal microscopy. The effect of phenytoin, carbamazepine and phenobarbital on CYP2E1 expression was evaluated in vivo or by using organotypic hippocampal cultures in vitro. CYP2E1 expression was investigated in brain resections from a cohort of drug-resistant epileptic brain resections and human endothelial cultures (EPI-EC). Immunohistochemistry showed an increase of CYP2E1 expression limited to hippocampal CA2/3 and hilar neurons after severe SE in mice. CYP2E1 expression was also observed at the astrocyte-vascular interface. Analysis of human brain specimens revealed CYP2E1 expression in neurons and vascular endothelial cells (EC). CYP2E1 was expressed in cultured human EC and over-expressed by EPI-EC. When analyzing the effect of drug exposure on CYP2E1 expression we found that, in vivo or in vitro, ethanol increased CYP2E1 levels in the brain and liver. Treatment with phenytoin induced localized CYP2E1 expression in the brain whereas no significant effects were exerted by carbamazepine or phenobarbital. Our data indicate that the effect of acute SE on brain CYP2E1 expression is localized and cell specific. Exposure to selected anti-epileptic drugs could play a role in determining CYP2E1 brain expression. Additional investigation is required to fully reproduce the culprits of P450 enzyme expression as observed in the human epileptic brain.
Keywords: CYP2E1; biotransformation; drug exposure; status epilepticus.
Copyright © 2014 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to declare. The authors have no relationships with organizations that could inappropriately influence, or be perceived to influence, the presented work.
Figures



References
-
- Abbott NJ, Khan EU, Rollinson CM, Reichel A, Janigro D, Dombrowski SM, Dobbie MS, Begley DJ. Drug resistance in epilepsy: the role of the blood-brain barrier. NovartisFoundSymp. 2002;243:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Bankstahl JP, Hoffmann K, Bethmann K, Loscher W. Glutamate is critically involved in seizure-induced overexpression of P-glycoprotein in the brain. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:1006–1016. - PubMed
-
- Bankstahl M, Bankstahl JP, Loscher W. Pilocarpine-induced epilepsy in mice alters seizure thresholds and the efficacy of antiepileptic drugs in the 6-Hertz psychomotor seizure model. Epilepsy research. 2013;107:205–216. - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Fricker G, Miller DS. Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier. MolPharmacol. 2004;66:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Yang X, Hartz AM, Olson ER, Zhao R, Kalvass JC, Pollack GM, Miller DS. In vivo activation of human pregnane X receptor tightens the blood-brain barrier to methadone through P-glycoprotein up-regulation. MolPharmacol. 2006;70:1212–1219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

