γδ T cell surveillance via CD1 molecules
- PMID: 25283967
- PMCID: PMC4383740
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2014.09.003
γδ T cell surveillance via CD1 molecules
Abstract
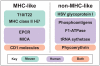
γδ T cells are a prominent epithelial-resident lymphocyte population, possessing multi-functional capacities in the repair of host tissue, pathogen clearance, and tumor surveillance. Although three decades have now passed since their discovery, the nature of γδ T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated ligand recognition remains poorly defined. Recent studies have provided structural insight into this recognition, demonstrating that γδ T cells survey both CD1 and the presented lipid, and in some cases are exquisitely lipid specific. We review these findings here, examining the molecular basis for and the functional relevance of this interaction. We discuss potential implications on the notion that non-classical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules may function as important restricting elements of γδ TCR specificity, and on our understanding of γδ T cell activation and function.
Keywords: CD1d; T cell receptor; crystallography; lipids; restriction; γδT cells.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Chien YH, et al. gammadelta T Cells: First Line of Defense and Beyond. Annu Rev Immunol. 2014;32:121–155. - PubMed
-
- McVay LD, Carding SR. Generation of human gammadelta T-cell repertoires. Crit Rev Immunol. 1999;19:431–460. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y, et al. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells. Nature. 1995;375:155–158. - PubMed
-
- Constant P, et al. Stimulation of human gamma delta T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science. 1994;264:267–270. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

