Probing formation of cargo/importin-α transport complexes in plant cells using a pathogen effector
- PMID: 25284001
- PMCID: PMC4350430
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.12691
Probing formation of cargo/importin-α transport complexes in plant cells using a pathogen effector
Abstract
Importin-αs are essential adapter proteins that recruit cytoplasmic proteins destined for active nuclear import to the nuclear transport machinery. Cargo proteins interact with the importin-α armadillo repeat domain via nuclear localization sequences (NLSs), short amino acids motifs enriched in Lys and Arg residues. Plant genomes typically encode several importin-α paralogs that can have both specific and partially redundant functions. Although some cargos are preferentially imported by a distinct importin-α it remains unknown how this specificity is generated and to what extent cargos compete for binding to nuclear transport receptors. Here we report that the effector protein HaRxL106 from the oomycete pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis co-opts the host cell's nuclear import machinery. We use HaRxL106 as a probe to determine redundant and specific functions of importin-α paralogs from Arabidopsis thaliana. A crystal structure of the importin-α3/MOS6 armadillo repeat domain suggests that five of the six Arabidopsis importin-αs expressed in rosette leaves have an almost identical NLS-binding site. Comparison of the importin-α binding affinities of HaRxL106 and other cargos in vitro and in plant cells suggests that relatively small affinity differences in vitro affect the rate of transport complex formation in vivo. Our results suggest that cargo affinity for importin-α, sequence variation at the importin-α NLS-binding sites and tissue-specific expression levels of importin-αs determine formation of cargo/importin-α transport complexes in plant cells.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis; importin-α; nuclear localization sequence; nucleo-cytoplasmic transport; oomycete effector; plant innate immunity.
© 2014 The Authors The Plant Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
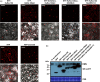



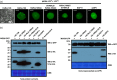
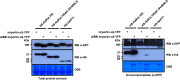
Similar articles
-
The truncated NLR protein TIR-NBS13 is a MOS6/IMPORTIN-α3 interaction partner required for plant immunity.Plant J. 2017 Dec;92(5):808-821. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13717. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28901644
-
Functional requirement of the Arabidopsis importin-α nuclear transport receptor family in autoimmunity mediated by the NLR protein SNC1.Plant J. 2021 Feb;105(4):994-1009. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15082. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 33210758
-
An importin alpha homolog, MOS6, plays an important role in plant innate immunity.Curr Biol. 2005 Jun 21;15(12):1129-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.022. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964279
-
IMPa-4, an Arabidopsis importin alpha isoform, is preferentially involved in agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation.Plant Cell. 2008 Oct;20(10):2661-80. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.060467. Epub 2008 Oct 3. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18836040 Free PMC article.
-
The importin β binding domain as a master regulator of nucleocytoplasmic transport.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Sep;1813(9):1578-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.10.012. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21029753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis downy mildew effector HaRxL106 suppresses plant immunity by binding to RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1.New Phytol. 2018 Oct;220(1):232-248. doi: 10.1111/nph.15277. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 30156022 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning the Wavelength: Manipulation of Light Signaling to Control Plant Defense.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 14;24(4):3803. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043803. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic Communication in Healthy and Diseased Plant Tissues.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jul 28;12:719453. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.719453. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34394173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential cargo proteins of transportin protein AtTRN1 in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Rep. 2016 Mar;35(3):629-40. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1908-4. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Plant Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26650834
-
A Poplar Rust Effector Protein Associates with Protein Disulfide Isomerase and Enhances Plant Susceptibility.Biology (Basel). 2020 Sep 16;9(9):294. doi: 10.3390/biology9090294. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32947987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfano JR, Charkowski AO, Deng WL, Badel JL, Petnicki-Ocwieja T, van Dijk K, Collmer A. The Pseudomonas syringae Hrp pathogenicity island has a tripartite mosaic structure composed of a cluster of type III secretion genes bounded by exchangeable effector and conserved effector loci that contribute to parasitic fitness and pathogenicity in plants. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:4856–4861. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asai S, Piquerez SJM, Rallapalli G, Caillaud M-C, Furzer O, Ishaque N, Wirthmueller L, Fabro G, Jones JDG. Expression profiling during Arabidopsis/downy mildew interaction reveals a highly-expressed effector that attenuates salicylic acid-triggered immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1004443. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai X, Correa VR, Toruño TY, Ammar E-D, Kamoun S, Hogenhout SA. AY-WB phytoplasma secretes a protein that targets plant cell nuclei. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009;22:18–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/K009176/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000C0624/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBJ00453/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBK009176/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

