Biomarkers for disease progression and AAV therapeutic efficacy in feline Sandhoff disease
- PMID: 25284324
- PMCID: PMC4262540
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.09.020
Biomarkers for disease progression and AAV therapeutic efficacy in feline Sandhoff disease
Abstract
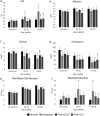
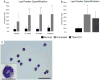
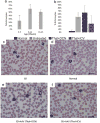
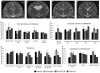
The GM2 gangliosidoses, Tay-Sachs disease (TSD) and Sandhoff disease (SD), are progressive neurodegenerative disorders that are caused by a mutation in the enzyme β-N-acetylhexosaminidase (Hex). Due to the recent emergence of novel experimental treatments, biomarker development has become particularly relevant in GM2 gangliosidosis as an objective means to measure therapeutic efficacy. Here we describe blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and electrodiagnostic methods for evaluating disease progression in the feline SD model and application of these approaches to assess AAV-mediated gene therapy. SD cats were treated by intracranial injections of the thalami combined with either the deep cerebellar nuclei or a single lateral ventricle using AAVrh8 vectors encoding feline Hex. Significantly altered in untreated SD cats, blood and CSF based biomarkers were largely normalized after AAV gene therapy. Also reduced after treatment were expansion of the lysosomal compartment in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and elevated activity of secondary lysosomal enzymes. MRI changes characteristic of the gangliosidoses were documented in SD cats and normalized after AAV gene therapy. The minimally invasive biomarkers reported herein should be useful to assess disease progression of untreated SD patients and those in future clinical trials.
Keywords: Biomarkers; GM2 ganglioside; Gene therapy; Hexosaminidase; Lysosomal storage disorder; Neurodegenerative disease.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
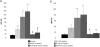

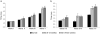
References
-
- Phaneuf D, Wakamatsu N, Huang JQ, Borowski A, Peterson AC, et al. Dramatically different phenotypes in mouse models of human Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Casal M, Haskins M. Large animal models and gene therapy. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14:266–272. - PubMed
-
- Aye MM, Izumo S, Inada S, Isashiki Y, Yamanaka H, et al. Histopathological and ultrastructural features of feline hereditary cerebellar cortical atrophy: a novel animal model of human spinocerebellar degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 1998;96:379–387. - PubMed
-
- Podell M, March PA, Buck WR, Mathes LE. The feline model of neuroAIDS: understanding the progression towards AIDS dementia. J Psychopharmacol. 2000;14:205–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

