MiRNA-30a inhibits AECs-II apoptosis by blocking mitochondrial fission dependent on Drp-1
- PMID: 25284615
- PMCID: PMC4302646
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12420
MiRNA-30a inhibits AECs-II apoptosis by blocking mitochondrial fission dependent on Drp-1
Abstract
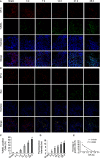
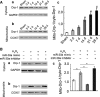
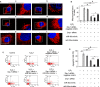
Apoptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECs-II) is a key determinant of initiation and progression of lung fibrosis. However, the mechanism of miR-30a participation in the regulation of AECs-II apoptosis is ambiguous. In this study, we investigated whether miR-30a could block AECs-II apoptosis by repressing mitochondrial fission dependent on dynamin-related protein-1 (Drp-1). The levels of miR-30a in vivo and in vitro were determined through quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The inhibition of miR-30a in AECs-II apoptosis, mitochondrial fission and its dependence on Drp-1, and Drp-1 expression and translocation were detected using miR-30a mimic, inhibitor-transfection method (gain- and loss-of-function), or Drp-1 siRNA technology. Results showed that miR-30a decreased in lung fibrosis. Gain- and loss-of-function studies revealed that the up-regulation of miR-30a could decrease AECs-II apoptosis, inhibit mitochondrial fission, and reduce Drp-1 expression and translocation. MiR-30a mimic/inhibitor and Drp-1 siRNA co-transfection showed that miR-30a could inhibit the mitochondrial fission dependent on Drp-1. This study demonstrated that miR-30a inhibited AECs-II apoptosis by repressing the mitochondrial fission dependent on Drp-1, and could function as a novel therapeutic target for lung fibrosis.
Keywords: AECs-II; Drp-1; apoptosis; lung fibrosis; miRNA-30a; mitochondrial fission.
© 2014 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures






References
-
- Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O. New cellular and molecular mechanisms of lung injury and fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2012;380:680–8. - PubMed
-
- Downey GP. Resolving the scar of pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1140–1. - PubMed
-
- Pandit KV, Milosevic J, Kaminski N. MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Transl Res. 2011;157:191–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

