Acceptability of bone antiresorptive therapy among HIV-infected adults at different stages of antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 25284989
- PMCID: PMC4181646
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S67090
Acceptability of bone antiresorptive therapy among HIV-infected adults at different stages of antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Both HIV infection and antiretroviral therapy (ART) are associated with significant decreases in bone mineral density (BMD) and increased fracture rates. To prepare for a randomized controlled trial of prophylactic bone antiresorptive therapy during ART initiation, we assessed the acceptability of this strategy, bone health knowledge, and fracture risk among HIV-infected adults.
Methods: HIV-infected adults with no history of osteoporosis were recruited from one tertiary and one primary care HIV clinic. Participants completed a questionnaire and underwent chart review. The primary outcome was the proportion of respondents expressing interest in taking prophylactic bone antiresorptive therapy in conjunction with ART.
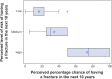
Results: Of 112 respondents, 25.0% were ART naïve, 23.2% had been taking ART for ≤1 year, and 51.8% had been taking ART for >1 year. Half (51.9%) indicated interest in taking short-course prophylactic bone antiresorptive therapy; this did not differ by ART status (53.6% among ART-naïve, 51.3% among ART-treated; P=0.84, chi-square test). In exploratory multivariable analysis adjusted for ART status, a greater number of pills taken per day was positively associated with this outcome (adjusted odds ratio [OR] =1.12 per pill, 95% confidence limit [CL] =1.01, 1.25), while male sex was inversely associated (adjusted OR =0.05, 95% CL =0.01, 0.24). Among those willing to take therapy, most (80.4%) were willing to do so for "as long as needed" and preferred weekly dosing (70.9%) to daily dosing (12.7%).
Conclusions: Half of this sample would be willing to take bone antiresorptive therapy together with ART, with preferences for weekly dosing and for whatever duration may be required. These data will inform the design of future trials to protect bone health in HIV.
Keywords: HIV; bone antiresorptive therapy; prophylaxis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utilization of DXA Bone Mineral Densitometry in Ontario: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(20):1-180. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074491 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced bone mineral density in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals: a meta-analysis of its prevalence and risk factors.Osteoporos Int. 2018 Mar;29(3):595-613. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-4305-8. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29159533
-
A Single-dose Zoledronic Acid Infusion Prevents Antiretroviral Therapy-induced Bone Loss in Treatment-naive HIV-infected Patients: A Phase IIb Trial.Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 1;63(5):663-671. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw331. Epub 2016 May 18. Clin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27193748 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antiretroviral therapy and the prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis: a meta-analytic review.AIDS. 2006 Nov 14;20(17):2165-74. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32801022eb. AIDS. 2006. PMID: 17086056 Review.
-
Effects of parathyroid hormone alone or in combination with antiresorptive therapy on bone mineral density and fracture risk--a meta-analysis.Osteoporos Int. 2007 Jan;18(1):45-57. doi: 10.1007/s00198-006-0204-0. Epub 2006 Sep 2. Osteoporos Int. 2007. PMID: 16951908 Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-effective osteoporosis treatment thresholds for people living with HIV infection in Greece.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017 Dec 1;17(4):292-298. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017. PMID: 29199188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown TT, Qaqish RB. Antiretroviral therapy and the prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis: a meta-analytic review. AIDS. 2006;20(17):2165–2174. - PubMed
-
- Bedimo R, Maalouf NM, Zhang S, Drechsler H, Tebas P. Osteoporotic fracture risk associated with cumulative exposure to tenofovir and other antiretroviral agents. AIDS. 2012;26(7):825–831. - PubMed
-
- Young B, Dao CN, Buchacz K, Baker R, Brooks JT, HIV Outpatient Study (HOPS) Investigators Increased rates of bone fracture among HIV-infected persons in the HIV Outpatient Study (HOPS) compared with the US general population, 2000–2006. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(8):1061–1068. - PubMed
-
- Amorosa V, Tebas P. Bone disease and HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:108–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources