Propofol prevents electroconvulsive-shock-induced memory impairment through regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity in a rat model of depression
- PMID: 25285008
- PMCID: PMC4181737
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S67108
Propofol prevents electroconvulsive-shock-induced memory impairment through regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity in a rat model of depression
Abstract
Background: Although a rapid and efficient psychiatric treatment, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) induces memory impairment. Modified ECT requires anesthesia for safety purposes. Although traditionally found to exert amnesic effects in general anesthesia, which is an inherent part of modified ECT, some anesthetics have been found to protect against ECT-induced cognitive impairment. However, the mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated the effects of propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol) on memory in depressed rats undergoing electroconvulsive shock (ECS), the analog of ECT in animals, under anesthesia as well as its mechanisms.
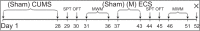
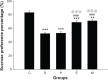
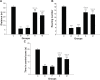
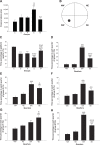
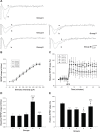
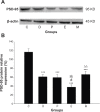
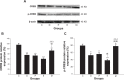
Methods: Chronic unpredictable mild stresses were adopted to reproduce depression in a rodent model. Rats underwent ECS (or sham ECS) with anesthesia with propofol or normal saline. Behavior was assessed in sucrose preference, open field and Morris water maze tests. Hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) was measured using electrophysiological techniques. PSD-95, CREB, and p-CREB protein expression was assayed with Western blotting.
Results: Depression induced memory damage, and downregulated LTP, PSD-95, CREB, and p-CREB; these effects were exacerbated in depressed rats by ECS; propofol did not reverse the depression-induced changes, but when administered in modified ECS, propofol improved memory and reversed the downregulation of LTP and the proteins.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that propofol prevents ECS-induced memory impairment, and modified ECS under anesthesia with propofol improves memory in depressed rats, possibly by reversing the excessive changes in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. These observations provide a novel insight into potential targets for optimizing the clinical use of ECT for psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: CREB; PSD-95; electroconvulsive therapy; long-term potentiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Propofol protects against impairment of learning-memory and imbalance of hippocampal Glu/GABA induced by electroconvulsive shock in depressed rats.J Anesth. 2011 Oct;25(5):657-65. doi: 10.1007/s00540-011-1199-z. Epub 2011 Jul 19. J Anesth. 2011. PMID: 21769668
-
Propofol ameliorates electroconvulsive shock-induced learning and memory impairment by regulation of synaptic metaplasticity via autophosphorylation of CaMKIIa at Thr 305 in stressed rats.Psychiatry Res. 2016 Jun 30;240:123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.03.053. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Psychiatry Res. 2016. PMID: 27104927
-
Propofol inhibits inflammatory cytokine-mediated glutamate uptake dysfunction to alleviate learning/memory impairment in depressed rats undergoing electroconvulsive shock.Brain Res. 2015 Jan 21;1595:101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.07.046. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25108038
-
Comparison of the effect of intravenous anesthetics used for anesthesia during electroconvulsive therapy on the hemodynamic safety and the course of ECT.Psychiatr Pol. 2017 Dec 30;51(6):1039-1058. doi: 10.12740/PP/75635. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Psychiatr Pol. 2017. PMID: 29432502 Review. English, Polish.
-
[ECT: from neuronal plasticity to mechanisms underlying antidepressant medication effect].Encephale. 2007 Sep;33(4 Pt 1):572-8. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(07)92055-2. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18033145 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective effect of miR-665 against sevoflurane anesthesia-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting insulin-like growth factor 2.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Mar 15;9(3):1344-1356. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28386360 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse repeated electroconvulsive seizure (ECS) does not reverse social stress effects but does induce behavioral and hippocampal changes relevant to electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) side-effects in the treatment of depression.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 14;12(9):e0184603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184603. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28910337 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in synaptic plasticity are associated with electroconvulsive shock-induced learning and memory impairment in rats with depression-like behavior.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018 Jul 2;14:1737-1746. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S163756. eCollection 2018. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018. PMID: 29997435 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of General Anesthetics on Synaptic Transmission.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(10):936-965. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200227125854. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32106800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of different charges of modified electroconvulsive seizure on the cognitive behavior in stressed rats: Effects of GluR1 phosphorylation and CaMKIIα activity.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jan;17(1):748-758. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7022. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30651859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goodman WK. Electroconvulsive therapy in the spotlight. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1785–1787. - PubMed
-
- Lisanby SH. Electroconvulsive therapy for depression. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(19):1939–1945. - PubMed
-
- Wani A, Trevino K, Marnell P, Husain MM. Advances in brain stimulation for depression. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2013;25(3):217–224. - PubMed
-
- Andrade C, Shaikh SA, Narayan L, Blasey C, Belanoff J. Administration of a selective glucocorticoid antagonist attenuates electroconvulsive shock-induced retrograde amnesia. J Neural Transm. 2012;119(3):337–344. - PubMed
-
- Sackeim HA, Prudic J, Devanand DP, et al. Effects of stimulus intensity and electrode placement on the efficacy and cognitive effects of electroconvulsive therapy. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(12):839–846. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

