Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the metabolic syndrome: Consequences of a dual threat
- PMID: 25285275
- PMCID: PMC4171881
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.139212
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the metabolic syndrome: Consequences of a dual threat
Abstract
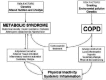
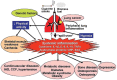
The metabolic syndrome is found to be more frequent in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The presence of inflammatory markers in circulation, sputum, and broncho-alveolar fluid suggest systemic inflammation is one of the potential mechanisms responsible for both COPD and metabolic syndrome. Physical inactivity, skeletal muscle dysfunction, hypogonadism, and steroid use are also important causes of the metabolic syndrome in COPD. Obesity and insulin resistance is found to be more common in mild to moderate stages (I and II) of COPD. Patients with COPD and the metabolic syndrome have increase risk of morbidity and mortality due to cardiovascular disease. This review describes in details the various components of metabolic syndrome and its impact on long outcomes in COPD patients.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; metabolic syndrome; physical inactivity; systemic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic bronchitis and COPD: frequency and associated consequences for systemic inflammation and physical inactivity.Chest. 2009 Oct;136(4):1039-1046. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-0393. Epub 2009 Jun 19. Chest. 2009. PMID: 19542257
-
Metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: frequency and relationship with systemic inflammation.Hippokratia. 2016 Apr-Jun;20(2):110-114. Hippokratia. 2016. PMID: 28416906 Free PMC article.
-
Physiopathological relationship between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and insulin resistance.Endocrine. 2018 Jul;61(1):17-22. doi: 10.1007/s12020-018-1554-z. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Endocrine. 2018. PMID: 29512058 Review.
-
Physical inactivity and obesity: relation to asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009 Dec;6(8):663-7. doi: 10.1513/pats.200907-070DP. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009. PMID: 20008872 Review.
-
Osteoporosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2015 Mar 12;9:5-21. doi: 10.4137/CCRPM.S22803. eCollection 2015. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2015. PMID: 25788838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Behavioral Risk Factors in Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases of the Lung Associated with Metabolic Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 11;13(4):1037. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041037. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38398353 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering Metabolic Syndrome among Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital, India.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 May;11(5):OC08-OC11. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/26488.9829. Epub 2017 May 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28658825 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Ketogenic Diet Is Associated With Improvements in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 29;8:699427. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.699427. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34395478 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of frequency of insulin resistance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with normal controls.Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Nov-Dec;31(6):1506-10. doi: 10.12669/pjms.316.7983. Pak J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26870125 Free PMC article.
-
Shared mechanisms of multimorbidity in COPD, atherosclerosis and type-2 diabetes: the neutrophil as a potential inflammatory target.Eur Respir Rev. 2020 Mar 20;29(155):190102. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0102-2019. Print 2020 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2020. PMID: 32198215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Shibuya K, Rao C, Mathers CD, Hansell AL, Held LS, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Current burden and future projections. Eur Respir J. 2006;27:397–412. - PubMed
-
- Halbert RJ, Natoli JL, Gano A, Badamgarav E, Buist AS, Mannino DM. Global burden of COPD: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2006;28:523–32. - PubMed
-
- Fukuchi Y, Nishimura M, Ichinose M, Adachi M, Nagai A, Kuriyama T, et al. COPD in Japan: The Nippon COPD Epidemiology study. Respirology. 2004;9:458–65. - PubMed
-
- Jindal SK, Aggarwal AN, Chaudhry K, Chhabra SK, D’ Souza GA, Gupta D, et al. A multicentric study on epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its relationship with tobacco smoking and environmental tobacco smoke exposure. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2006;48:23–9. - PubMed

