Structural and energetic effects of A2A adenosine receptor mutations on agonist and antagonist binding
- PMID: 25285959
- PMCID: PMC4186821
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108492
Structural and energetic effects of A2A adenosine receptor mutations on agonist and antagonist binding
Abstract
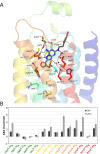
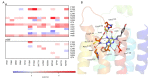
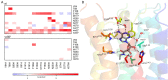
To predict structural and energetic effects of point mutations on ligand binding is of considerable interest in biochemistry and pharmacology. This is not only useful in connection with site-directed mutagenesis experiments, but could also allow interpretation and prediction of individual responses to drug treatment. For G-protein coupled receptors systematic mutagenesis has provided the major part of functional data as structural information until recently has been very limited. For the pharmacologically important A(2A) adenosine receptor, extensive site-directed mutagenesis data on agonist and antagonist binding is available and crystal structures of both types of complexes have been determined. Here, we employ a computational strategy, based on molecular dynamics free energy simulations, to rationalize and interpret available alanine-scanning experiments for both agonist and antagonist binding to this receptor. These computer simulations show excellent agreement with the experimental data and, most importantly, reveal the molecular details behind the observed effects which are often not immediately evident from the crystal structures. The work further provides a distinct validation of the computational strategy used to assess effects of point-mutations on ligand binding. It also highlights the importance of considering not only protein-ligand interactions but also those mediated by solvent water molecules, in ligand design projects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
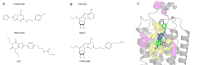


Similar articles
-
Bridging molecular docking to membrane molecular dynamics to investigate GPCR-ligand recognition: the human A₂A adenosine receptor as a key study.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Jan 27;54(1):169-83. doi: 10.1021/ci400532b. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24359090
-
Agonist-bound adenosine A2A receptor structures reveal common features of GPCR activation.Nature. 2011 May 18;474(7352):521-5. doi: 10.1038/nature10136. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21593763 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Role of the G Protein in Stabilizing the Active State of the Adenosine A2A Receptor.Structure. 2019 Apr 2;27(4):703-712.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.12.007. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Structure. 2019. PMID: 30713025 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approaches for targeting the adenosine A2A receptor.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015 Jan;10(1):63-80. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2015.971006. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 25311639 Review.
-
Recent Advances in the In-silico Structure-based and Ligand-based Approaches for the Design and Discovery of Agonists and Antagonists of A2A Adenosine Receptor.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(7):774-782. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190306162006. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30848185 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of chronic ulcer in diabetic rats with self assembling nanofiber gel encapsulated-polydeoxyribonucleotide.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Jul 15;8(7):3067-76. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27508027 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of 2-aryl benzoxazoles as promising hit for the A2A receptor.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017 Dec;32(1):850-864. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1334648. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28661196 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering conformational selectivity in the A2A adenosine G protein-coupled receptor by free energy simulations.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Nov 24;17(11):e1009152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009152. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34818333 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Drug Design for Purinergic GPCRs: Overview on Molecular Dynamics Applied to Adenosine and P2Y Receptors.Biomolecules. 2020 May 26;10(6):812. doi: 10.3390/biom10060812. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32466404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of V6.51L as a selectivity hotspot in stereoselective A2B adenosine receptor antagonist recognition.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 8;11(1):14171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93419-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34238993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hopkins AL, Groom CR (2002) The druggable genome. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1: 727–730. - PubMed
-
- Venkatakrishnan AJ, Deupi X, Lebon G, Tate CG, Schertler GF, et al. (2013) Molecular signatures of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 494: 185–194. - PubMed
-
- Gutiérrez-de-Terán H (2014) The roles of computational chemistry in the ligand design of G protein-coupled receptors: how far have we come and what should we expect? Future Med Chem 6: 251–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

