Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules
- PMID: 25286013
- PMCID: PMC4387118
- DOI: 10.1039/c4cs00280f
Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules
Abstract
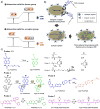
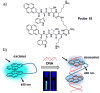
Quantitative determination of specific analytes is essential for a variety of applications ranging from life sciences to environmental monitoring. Optical sensing allows non-invasive measurements within biological milieus, parallel monitoring of multiple samples, and less invasive imaging. Among the optical sensing methods currently being explored, ratiometric fluorescence sensing has received particular attention as a technique with the potential to provide precise and quantitative analyses. Among its advantages are high sensitivity and inherent reliability, which reflect the self-calibration provided by monitoring two (or more) emissions. A wide variety of ratiometric sensing probes using small fluorescent molecules have been developed for sensing, imaging, and biomedical applications. In this research highlight, we provide an overview of the design principles underlying small fluorescent probes that have been applied to the ratiometric detection of various analytes, including cations, anions, and biomolecules in solution and in biological samples. This highlight is designed to be illustrative, not comprehensive.
Figures
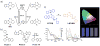

References
-
- de Silva AP, Gunaratne HQN, Gunnlaugsson T, Huxley AJM, McCoy CP, Rademacher JT, Rice TE. Chem Rev. 1997;97:1515. - PubMed
-
- Kim JS, Quang DT. Chem Rev. 2007;107:3780. - PubMed
-
- Nolan EM, Lippard SJ. Chem Rev. 2008;108:3443. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Zhou Y, Peng X, Yoon J. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:2120. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Xu Z, Yoon J. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:2222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

