Improved measurement of brain deformation during mild head acceleration using a novel tagged MRI sequence
- PMID: 25287113
- PMCID: PMC4254110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2014.09.010
Improved measurement of brain deformation during mild head acceleration using a novel tagged MRI sequence
Abstract
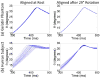
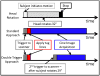
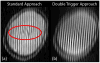
In vivo measurements of human brain deformation during mild acceleration are needed to help validate computational models of traumatic brain injury and to understand the factors that govern the mechanical response of the brain. Tagged magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful, noninvasive technique to track tissue motion in vivo which has been used to quantify brain deformation in live human subjects. However, these prior studies required from 72 to 144 head rotations to generate deformation data for a single image slice, precluding its use to investigate the entire brain in a single subject. Here, a novel method is introduced that significantly reduces temporal variability in the acquisition and improves the accuracy of displacement estimates. Optimization of the acquisition parameters in a gelatin phantom and three human subjects leads to a reduction in the number of rotations from 72 to 144 to as few as 8 for a single image slice. The ability to estimate accurate, well-resolved, fields of displacement and strain in far fewer repetitions will enable comprehensive studies of acceleration-induced deformation throughout the human brain in vivo.
Keywords: Acceleration; Deformation; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); Strain; Traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Andrew Knutsen, Elizabeth Magrath, Julie McEntee, Philip Bayly, John Butman, and Dzung Pham have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Jerry Prince is a founder and stock holder in Diagnosoft, Inc., which has licensed the HARP motion estimation technology from Johns Hopkins University. The terms of this arrangement are being managed by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures

References
-
- Abd-Elmoniem KZ, Osman NF, Prince JL, Stuber M. Three-dimensional magnetic resonance myocardial motion tracking from a single image plane. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2007;58:92–102. - PubMed
-
- Abd-Elmoniem KZ, Stuber M, Osman NF, Prince JL. ZHARP: three-dimensional motion tracking from a single image plane. Information Processing in Medical Imaging. 2005;19:639–651. - PubMed
-
- Augenstein KF, Cowan BR, LeGrice IJ, Nielsen PM, Young AA. Method and apparatus for soft tissue material parameter estimation using tissue tagged Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 2005;127:148–157. - PubMed
-
- Axel L, Dougherty L. MR imaging of motion with spatial modulation of magnetization. Radiology. 1989;171:841–845. - PubMed
-
- Baugh CM, Stamm JM, Riley DO, Gavett BE, Shenton ME, Lin A, Nowinski CJ, Cantu RC, McKee AC, Stern RA. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy: neurodegeneration following repetitive concussive and subconcussive brain trauma. Brain Imaging Behavior. 2012;6:244–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

