Multifunctional, stimuli-sensitive nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery
- PMID: 25287120
- PMCID: PMC4489143
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd4333
Multifunctional, stimuli-sensitive nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery
Abstract
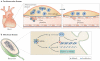
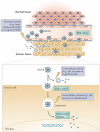
The use of nanoparticulate pharmaceutical drug delivery systems (NDDSs) to enhance the in vivo effectiveness of drugs is now well established. The development of multifunctional and stimulus-sensitive NDDSs is an active area of current research. Such NDDSs can have long circulation times, target the site of the disease and enhance the intracellular delivery of a drug. This type of NDDS can also respond to local stimuli that are characteristic of the pathological site by, for example, releasing an entrapped drug or shedding a protective coating, thus facilitating the interaction between drug-loaded nanocarriers and target cells or tissues. In addition, imaging contrast moieties can be attached to these carriers to track their real-time biodistribution and accumulation in target cells or tissues. Here, I highlight recent developments with multifunctional and stimuli-sensitive NDDSs and their therapeutic potential for diseases including cancer, cardiovascular diseases and infectious diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Torchilin VP, editor. Nanoparticulates as Drug Carriers. Imperial College Press; 2006.
-
- Thassu D, Deleers M. In: Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems. Pathak Y, editor. Informa Healthcare USA; 2007.
-
- Ferrari M. Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nature Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:161–171. - PubMed
-
- van Vlerken LE, Amiji MM. Multi-functional polymeric nanoparticles for tumour-targeted drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006;3:205–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

