Blood pressure and risk of all-cause mortality in advanced chronic kidney disease and hemodialysis: the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study
- PMID: 25287404
- PMCID: PMC4268143
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04334
Blood pressure and risk of all-cause mortality in advanced chronic kidney disease and hemodialysis: the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study
Abstract
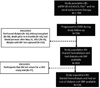
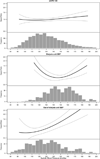
Studies of hemodialysis patients have shown a U-shaped association between systolic blood pressure (SBP) and mortality. These studies have largely relied on dialysis-unit SBP measures and have not evaluated whether this U-shape also exists in advanced chronic kidney disease, before starting hemodialysis. We determined the association between SBP and mortality at advanced chronic kidney disease and again after initiation of hemodialysis. This was a prospective study of Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort participants with advanced chronic kidney disease followed through initiation of hemodialysis. We studied the association between SBP and mortality when participants (1) had an estimated glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n=1705), (2) initiated hemodialysis and had dialysis-unit SBP measures (n=403), and (3) initiated hemodialysis and had out-of-dialysis-unit SBP measured at a Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study visit (n=326). Cox models were adjusted for demographics, cardiovascular risk factors, and dialysis parameters. A quadratic term for SBP was included to test for a U-shaped association. At advanced chronic kidney disease, there was no association between SBP and mortality (hazard ratio, 1.02 [95% confidence interval, 0.98-1.07] per every 10 mm Hg increase). Among participants who started hemodialysis, a U-shaped association between dialysis-unit SBP and mortality was observed. In contrast, there was a linear association between out-of-dialysis-unit SBP and mortality (hazard ratio, 1.26 [95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.40] per every 10 mm Hg increase). In conclusion, more efforts should be made to obtain out-of-dialysis-unit SBP, which may merit more consideration as a target for clinical management and in interventional trials.
Keywords: CKD; ESRD; dialysis; hypertension; mortality.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Blood pressure in chronic kidney disease: does the emperor have new clothes?Hypertension. 2015 Jan;65(1):27-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04449. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25287402 No abstract available.
References
-
- Peralta CA, Hicks LS, Chertow GM, Ayanian JZ, Vittinghoff E, Lin F, Shlipak MG. Control of hypertension in adults with chronic kidney disease in the united states. Hypertension. 2005;45:1119–1124. - PubMed
-
- Levin NW, Kotanko P, Eckardt KU, Kasiske BL, Chazot C, Cheung AK, Redon J, Wheeler DC, Zoccali C, London GM. Blood pressure in chronic kidney disease stage 5d-report from a kidney disease: Improving global outcomes controversies conference. Kidney Int. 2010;77:273–284. - PubMed
-
- Klahr S, Levey AS, Beck GJ, Caggiula AW, Hunsicker L, Kusek JW, Striker G. The effects of dietary protein restriction and blood-pressure control on the progression of chronic renal disease. Modification of diet in renal disease study group. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:877–884. - PubMed
-
- Agodoa LY, Appel L, Bakris GL, Beck G, Bourgoignie J, Briggs JP, Charleston J, Cheek D, Cleveland W, Douglas JG, Douglas M, Dowie D, Faulkner M, Gabriel A, Gassman J, Greene T, Hall Y, Hebert L, Hiremath L, Jamerson K, Johnson CJ, Kopple J, Kusek J, Lash J, Lea J, Lewis JB, Lipkowitz M, Massry S, Middleton J, Miller ER, 3rd, Norris K, O'Connor D, Ojo A, Phillips RA, Pogue V, Rahman M, Randall OS, Rostand S, Schulman G, Smith W, Thornley-Brown D, Tisher CC, Toto RD, Wright JT, Jr, Xu S. Effect of ramipril vs amlodipine on renal outcomes in hypertensive nephrosclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;285:2719–2728. - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Gherardi G, Garini G, Zoccali C, Salvadori M, Scolari F, Schena FP, Remuzzi G. Renoprotective properties of ace-inhibition in non-diabetic nephropathies with non-nephrotic proteinuria. Lancet. 1999;354:359–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK92291/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK088865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK70939/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK092353/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070939/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR-000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-16500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK092291/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

