Up-regulation of hexokinase1 in the right ventricle of monocrotaline induced pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 25287584
- PMCID: PMC4198683
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-014-0119-9
Up-regulation of hexokinase1 in the right ventricle of monocrotaline induced pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a proliferative arteriopathy associated with a glycolytic shift during heart metabolism. An increase in glycolytic metabolism can be detected in the right ventricle during PAH. Expression levels of glycolysis genes in the right ventricle during glycolysis that occur in monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) remain unknown.
Methods: PH was induced by a single subcutaneous injection of MCT (50 mg/kg) into rats, eventually causing right heart failure. Concurrently, a control group was injected with normal saline. The MCT-PH rats were randomly divided into three groups according to MCT treatment: MCT-2 week, 3 week, and 4 week groups (MCT-2w, 3w, 4w). At the end of the study, hemodynamics and right ventricular hypertrophy were compared among experimental groups. Expression of key glycolytic candidate genes was screened in the right ventricle.
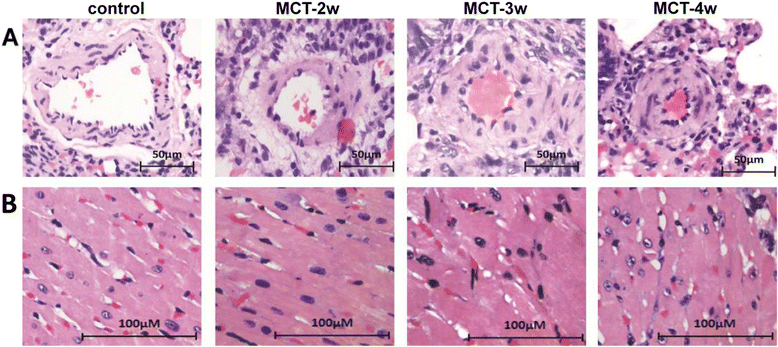
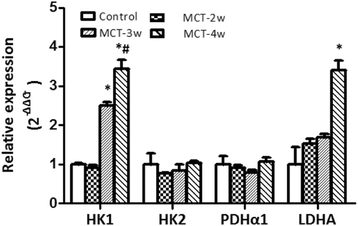
Results: We observed an increase in mean pulmonary arterial pressure, right ventricular systolic pressure and right ventricular hypertrophy index three weeks following MCT injection. Alterations in the morphology and structure of right ventricular myocardial cells, as well as the pulmonary vasculature were observed. Expression of hexokinase 1 (HK1) mRNA began to increase in the right ventricle of the MCT-3w group and MCT-4w group, while the expression of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) was elevated in the right ventricle of the MCT-4w group. Hexokinase 2(HK2), pyruvate dehydrogenase complex α1 (PDHα1), and LDHA mRNA expression showed no changes in the right ventricle. HK1 mRNA expression was further confirmed by HK1 protein expression and immunohistochemical analyses. All findings underlie the glycolytic phenotype in the right ventricle.
Conclusions: There was an increase in the protein and mRNA expression of hexokinase-1 (HK1) three and four weeks after the injection of monocrotaline in the right ventricle, intervention of HK1 may be amenable to therapeutic intervention.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Glycoltic metabolism gene changes in left and right ventricles in experimental rat pulmonary arterial hypertension model].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;42(12):1010-6. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25623347 Chinese.
-
Pulmonary arterial hypertension induced by a novel method: Twice-intraperitoneal injection of monocrotaline.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Aug;243(12):995-1003. doi: 10.1177/1535370218794128. Epub 2018 Aug 12. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30099957 Free PMC article.
-
Urantide improves the structure and function of right ventricle as determined by echocardiography in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension rat model.Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Jan;38(1):29-35. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-3978-5. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 29362961
-
The Monocrotaline Rat Model of Right Heart Disease Induced by Pulmonary Artery Hypertension.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 23;12(9):1944. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091944. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of genetically-driven rodent models of pulmonary hypertension.Vascul Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;144:106970. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2022.106970. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Vascul Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35150934 Review.
Cited by
-
cAMP-PKA-CaMKII signaling pathway is involved in aggravated cardiotoxicity during Fuzi and Beimu Combination Treatment of Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 14;6:34903. doi: 10.1038/srep34903. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27739450 Free PMC article.
-
Increased in vivo mitochondrial oxygenation with right ventricular failure induced by pulmonary arterial hypertension: mitochondrial inhibition as driver of cardiac failure?Respir Res. 2015 Feb 3;16(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0178-6. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 25645252 Free PMC article.
-
Isolated Left Atrium Morphofunctional Study of an Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension Model in Rats.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Sep;120(10):e20230188. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230188. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37878960 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Identification of Key Players Involved in CoCl2 Hypoxia Induced Pulmonary Artery Hypertension in vitro.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 24;11:232. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00232. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32391042 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Remodeling in the Pressure-Loaded Right Ventricle: Shifts in Glucose and Fatty Acid Metabolism-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Nov 5;8(21):e012086. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012086. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31657265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gomez-Arroyo J, Sandoval J, Simon MA, Dominguez-Cano E, Voelkel NF, Bogaard HJ: Treatment for pulmonary arterial hypertension-associated right ventricular dysfunction.Ann Am Thorac Soc 2014, ᅟ:ᅟ [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
-
- Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Haddad F, Chin KM, Forfia PR, Kawut SM, Lumens J, Naeije R, Newman J, Oudiz RJ, Provencher S, Torbicki A, Voelkel NF, Hassoun PM. Right heart adaptation to pulmonary arterial hypertension: physiology and pathobiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D22–D33. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oikawa M, Kagaya Y, Otani H, Sakuma M, Demachi J, Suzuki J, Takahashi T, Nawata J, Ido T, Watanabe J, Shirato K. Increased [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation in right ventricular free wall in patients with pulmonary hypertension and the effect of epoprostenol. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:1849–1855. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.02.065. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

