miR-150 modulates cisplatin chemosensitivity and invasiveness of muscle-invasive bladder cancer cells via targeting PDCD4 in vitro
- PMID: 25287716
- PMCID: PMC4199406
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.891340
miR-150 modulates cisplatin chemosensitivity and invasiveness of muscle-invasive bladder cancer cells via targeting PDCD4 in vitro
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapeutic insensitivity and tumor cell invasiveness are major obstacles to effectively treating muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). Recent reports show that microRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in the chemotherapeutic response and disease progression of MIBC. Therefore, here we investigated the role of miR-150 in MIBC cells in vitro.
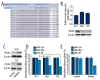
Material and methods: miR-150 expression was quantified by qRT-PCR in two MIBC cell lines (5637 and T24). After successful miR-150 inhibition by transfection, MTS and transwell assays were used to assess the MIBC's cisplatin sensitivity and cell invasiveness, respectively. The TargetScan database and a luciferase reporter system were used to identify whether the programmed cell death 4 protein (PDCD4) is a direct target of miR-150 in MIBC cells.
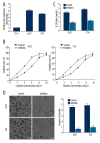
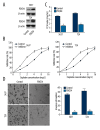
Results: miR-150 expression was found to be significantly increased in both MIBC cell lines, and treatment with a miR-150 inhibitor significantly sensitized MIBC cells to cisplatin and inhibited MIBC cell invasiveness. PDCD4 was identified as a direct target of miR-150 in MIBC cells, and increased PDCD4 expression via transfection with the pLEX-PDCD4 plasmid efficiently sensitized MIBC cells to cisplatin chemotherapy and inhibited MIBC cell invasiveness.
Conclusions: This study provides novel evidence that miR-150 functions as a tumor promoter in reducing chemosensitivity and promoting invasiveness of MIBC cells via targeting PDCD4. Thus, modulation of the miR-150-PDCD4 axis shows promise as a therapeutic strategy for MIBC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maspin enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity in bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells and correlates with prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients receiving cisplatin based neoadjuvant chemotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 6;35:2. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0282-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26733306 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-induced epigenetic activation of miR-34a sensitizes bladder cancer cells to chemotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2014 Jan 15;13:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-8. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24423412 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-141 reverses cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via upregulation of programmed cell death protein 4.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jun;20(12):2565-72. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27383306
-
miR-101 suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor C that inhibits migration and invasion and enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity of bladder cancer cells.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117809. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658842 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-21 modulates chemosensitivity of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin by targeting PDCD4.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 May;390(1-2):253-62. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-1976-8. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24609942
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNA transcripts, incredible modulators of cisplatin chemo-resistance in bladder cancer through operating a broad spectrum of cellular processes and signaling mechanism.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Jan 22;9(2):560-582. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.009. eCollection 2024 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38515791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Bladder Cancer: From Dark Matter to Valuable Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 13;18(7):1514. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071514. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28703782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-150 enhances apoptotic and anti-tumor effects of paclitaxel in paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cells by targeting Notch3.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 18;8(42):72788-72800. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20348. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29069826 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of miR-9 target CBX7 to regulate invasion ability of bladder transitional cell carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jan 18;21:225-30. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893232. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 25596753 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead Box R2 Knockdown Decreases Chemoresistance to Cisplatin via MYC Pathway in Bladder Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 25;25:8928-8939. doi: 10.12659/MSM.917345. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31761897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Botteman MF, Pashos CL, Redaelli A, et al. The health economics of bladder cancer: a comprehensive review of the published literature. Pharmacoeconomics. 2003;21:1315–30. - PubMed
-
- Shah JB, McConkey DJ, Dinney CP. New strategies in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: on the road to personalized medicine. CLin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2608–12. - PubMed
-
- Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, et al. Treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: update of the EAU guidelines. Eur Urol. 2011;59:1009–18. - PubMed
-
- Herr HW, Dotan Z, Donat SM, et al. Defining optimal therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Urology. 2007;177:437–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

