Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis
- PMID: 25287933
- PMCID: PMC4491294
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09750913
Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis
Erratum in
-
Correction. Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Oct 7;10(10):1886-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08840815. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26384363 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
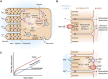
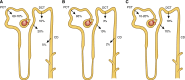
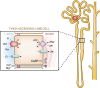
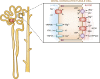
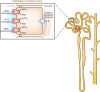
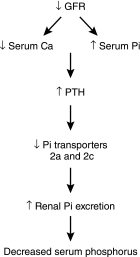
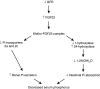
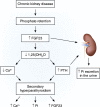
Calcium, phosphate, and magnesium are multivalent cations that are important for many biologic and cellular functions. The kidneys play a central role in the homeostasis of these ions. Gastrointestinal absorption is balanced by renal excretion. When body stores of these ions decline significantly, gastrointestinal absorption, bone resorption, and renal tubular reabsorption increase to normalize their levels. Renal regulation of these ions occurs through glomerular filtration and tubular reabsorption and/or secretion and is therefore an important determinant of plasma ion concentration. Under physiologic conditions, the whole body balance of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium is maintained by fine adjustments of urinary excretion to equal the net intake. This review discusses how calcium, phosphate, and magnesium are handled by the kidneys.
Keywords: calcium; cell and transport physiology; channel; electrolytes; ion; renal physiology.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Kumar R: Calcium metabolism. In: The Principles and Practice of Nephrology, edited by Jacobson HR, Striker GE, Klahr S, 2nd Ed., St. Louis, MO, Mosby-Year Book, 1995, pp 964–971
-
- Hebert SC, Brown EM: The scent of an ion: Calcium-sensing and its roles in health and disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 5: 45–53, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Johnson JA, Kumar R: Renal and intestinal calcium transport: Roles of vitamin D and vitamin D-dependent calcium binding proteins. Semin Nephrol 14: 119–128, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Kumar R: Calcium transport in epithelial cells of the intestine and kidney. J Cell Biochem 57: 392–398, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Keller J, Schinke T: The role of the gastrointestinal tract in calcium homeostasis and bone remodeling. Osteoporos Int 24: 2737–2748, 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

