Significantly decreased and more variable expression of major CYPs and UGTs in liver microsomes prepared from HBV-positive human hepatocellular carcinoma and matched pericarcinomatous tissues determined using an isotope label-free UPLC-MS/MS method
- PMID: 25288013
- PMCID: PMC7728448
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-014-1525-x
Significantly decreased and more variable expression of major CYPs and UGTs in liver microsomes prepared from HBV-positive human hepatocellular carcinoma and matched pericarcinomatous tissues determined using an isotope label-free UPLC-MS/MS method
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the liver expression of cytochrome P450 (CYPs) and uridine 5'-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), the major phase I and II metabolism enzymes responsible for clearance and detoxification of drugs, xenobiotic and endogenous substances.
Methods: A validated isotope label-free method was established for absolute and simultaneous quantification of 9 CYPs (1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D, 2E1 and 3A4) and 5 UGTs (1A1, 1A4, 1A6, 1A9 and 2B7) in human liver microsomes using LC-MS/MS.
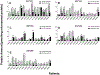
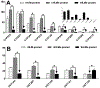
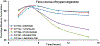
Results: The LC-MS/MS method displayed excellent dynamic range (at least 250-fold) and high sensitivity for each of the signature peptides with acceptable recovery, accuracy and precision. The protein expression profile of CYP and UGT isoforms were then determined in match microsomes samples prepared from patients with HBV-positive human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In the tumor microsomes, the average absolute amounts of 8 major CYP isoforms (except CYP2C19) and 3 UGT isoforms (UGT1A1, UGT1A4 and UGT2B7) were decreased significantly (p < 0.05), whereas UGT1A6 and UGT1A9 levels were unchanged (p > 0.05). In addition, among isoforms with altered expression, 6 of 8 CYP isoforms and all three UGT isoforms were much more variable in tumor microsomes. Lastly, the importance of CYP3A4 was greatly diminished whereas the importance of UGT1A6 was enhanced in tumor microsomes.
Conclusion: The use of an isotope label-free absolute quantification method for the simultaneous determination of 9 CYPs and 5 UGTs in human liver microsomes reveals that expression levels of CYPs and UGTs in human liver are severely impact by HCC, which could impact drug metabolism, disposition and pharmacotherapy.
Figures





Similar articles
-
AM-2201 Inhibits Multiple Cytochrome P450 and Uridine 5'-Diphospho-Glucuronosyltransferase Enzyme Activities in Human Liver Microsomes.Molecules. 2017 Mar 10;22(3):443. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030443. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28287454 Free PMC article.
-
Absolute quantification of UGT1A1 in various tissues and cell lines using isotope label-free UPLC-MS/MS method determines its turnover number and correlates with its glucuronidation activities.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;88:180-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.08.024. Epub 2013 Aug 29. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 24055854 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cytochrome P450 and uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases by MAM-2201 in human liver microsomes.Arch Pharm Res. 2017 Jun;40(6):727-735. doi: 10.1007/s12272-017-0917-y. Epub 2017 May 8. Arch Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28484907
-
Renal drug metabolism in humans: the potential for drug-endobiotic interactions involving cytochrome P450 (CYP) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT).Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;76(4):587-602. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12086. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23362865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress in quantitative methods based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for drug metabolizing enzymes in human liver microsomes].Se Pu. 2015 Jun;33(6):553-7. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1123.2015.03023. Se Pu. 2015. PMID: 26536756 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
CYP2E1 plays a suppressive role in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating Wnt/Dvl2/β-catenin signaling.J Transl Med. 2022 May 4;20(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03396-6. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35509083 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Issues and Optimized Practices in Quantification of Protein Abundance Level to Determine Interindividual Variability in DMET Proteins by LC-MS/MS Proteomics.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;103(4):619-630. doi: 10.1002/cpt.819. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 28833066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative profiling of human renal UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and glucuronidation activity: a comparison of normal and tumoral kidney tissues.Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Apr;43(4):611-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.114.062877. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015. PMID: 25650382 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomics of Hepatic Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters in Patients With Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Sep;112(3):699-710. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2633. Epub 2022 May 21. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35510337 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced oxidation protein products downregulate CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 expression and activity via the NF-κB-mediated signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.Lab Invest. 2021 Sep;101(9):1197-1209. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00610-9. Epub 2021 May 24. Lab Invest. 2021. PMID: 34031539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma RR. Enzyme Inhibition and Bioapplications In: Badal S, Shields M, Delgoda R, editors. Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Inhibitors, Nature InTech, 2012, p. 39–56.
-
- Rowland A, Miners JO, Mackenzie PI. The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: their role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45:1121–32. - PubMed
-
- Special Issue: The 64th Annual Meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: The Liver Meeting 2013. HBV Epidemiology and Prevention. Hepatology. 2013;58:607A–26A.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

