Heterogeneity of mprF sequences in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates: role in cross-resistance between daptomycin and host defense antimicrobial peptides
- PMID: 25288091
- PMCID: PMC4249560
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.03422-14
Heterogeneity of mprF sequences in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates: role in cross-resistance between daptomycin and host defense antimicrobial peptides
Abstract
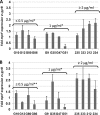
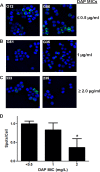
Over the past several years, single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the mprF open reading frame (ORF) have been proposed to be associated with a gain-of-function phenotype in terms of daptomycin (DAP) nonsusceptibility (referred to as daptomycin resistance [DAP-R] herein for ease of presentation) in Staphylococcus aureus. We investigated the frequencies of SNPs within the mprF ORF and the relationships of such SNPs to cross-resistance between DAP and cationic host defense peptides (HDPs). Thirty-five well-characterized, unique DAP-susceptible (DAP-S) and DAP-R methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) isolates of the clonal complex 5 genotype were used. In addition to mprF SNPs and DAP-HDP cross-resistance, several other key genotypic and phenotypic metrics often associated with DAP-R were delineated, as follows: (i) mprF expression, (ii) membrane phospholipid content, (iii) positive surface charge, (iv) DAP binding, and (v) cell wall thickness profiles. A number of DAP-S strains (MICs of ≤ 1 μg/ml) exhibited mprF SNPs, occasionally with high-level mprF sequence variation from the genotype reference strain. However, none of these SNPs were localized to well-chronicled mprF hot spot locations associated with DAP-R in S. aureus. In contrast, all 8 DAP-R isolates demonstrated SNPs within such known mprF hot spots. Moreover, only the DAP-R strains showed MprF gain-of-function phenotypes, enhanced mprF expression, higher survival against two prototypical HDPs, and reduced DAP binding. Although a heterogenous array of mprF SNPs were often found in DAP-S strains, only selected hot spot SNPs, combined with concurrent mprF dysregulation, were associated with the DAP-R phenotype.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Jones T, Yeaman MR, Sakoulas G, Yang SJ, Proctor RA, Sahl HG, Schrenzel J, Xiong YQ, Bayer AS. 2008. Failures in clinical treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infection with daptomycin are associated with alterations in surface charge, membrane phospholipid asymmetry, and drug binding. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52:269–278. 10.1128/AAC.00719-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

