Cardiovascular effects of resveratrol and atorvastatin treatments in an H2O2-induced stress model
- PMID: 25289077
- PMCID: PMC4186369
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1956
Cardiovascular effects of resveratrol and atorvastatin treatments in an H2O2-induced stress model
Abstract
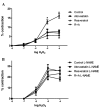
Oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathophysiology of several types of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Statins are widely used to inhibit the progression of atherosclerosis and reduce the incidence of CVD. Certain over-the-counter products, including resveratrol, show similar effects to statins and may thus be used in conjunction with statins for the treatment of the majority of patients with CVD. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of atorvastatin, resveratrol and resveratrol + atorvastatin (R+A) pretreatment on myocardial contractions and vascular endothelial functions in the presence of H2O2 as an experimental model of oxidative stress in rats. Four groups were established and referred to as the control, atorvastatin, resveratrol and R+A groups. Atorvastatin (40 mg/kg, per oral) and/or resveratrol (30 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) treatments were administered for 14 days. On the 15th day, the thoracic aortas and hearts of the rats were dissected and placed into isolated organ baths. Vascular responses to cumulative doses of H2O2 (1×10-8-1×10-4 M H2O2) with and without N (G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) incubation were measured. In addition, myocardial electrical stimulation (ES) responses to various H2O2 concentrations (1×10-7-1×10-5 M H2O2) were evaluated. In the control and atorvastatin groups, H2O2 application caused a significant dose-dependent decrease in the ES-induced contractions in the myocardial tissue of rats. In the resveratrol and R+A groups, H2O2 application did not significantly affect myocardial contraction at any dose. In all groups, incubation with L-NAME caused a significant augmentation in the H2O2 response, revealing that this effect was mediated via the vascular endothelium. In conclusion, pretreatment with R+A for CVD appears to be superior to pretreatment with either agent alone.
Keywords: atorvastatin; endothelium; hydrogen peroxide; myocardium; resveratrol.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cilostazol enhances atorvastatin-induced vasodilation of female rat aorta during aging.Physiol Int. 2017 Sep 1;104(3):226-234. doi: 10.1556/2060.104.2017.3.3. Physiol Int. 2017. PMID: 28956637
-
COX-2 inhibitor nimesulide protects rat heart against oxidative stress by improving endothelial function and enhancing NO production.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2007 Oct 25;59(5):674-80. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17940709
-
Cooling and response to hydrogen peroxide in human saphenous vein: role of the endothelium.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Jun;19(3):341-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2005.00330.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15910658
-
Increased activity of H2O2 in aorta isolated from chronically streptozotocin-diabetic rats: effects of antioxidant enzymes and enzymes inhibitors.Free Radic Biol Med. 1999 Jul;27(1-2):16-27. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(99)00028-3. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10443915
-
Effects of dietary polyphenols on gene expression in human vascular endothelial cells.Proc Nutr Soc. 2008 Feb;67(1):42-7. doi: 10.1017/S0029665108006009. Proc Nutr Soc. 2008. PMID: 18234130 Review.
Cited by
-
Lovastatin and Resveratrol Synergistically Improve Wound Healing and Inhibit Bacterial Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 20;26(2):851. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020851. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859566 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-N'-(1-(7-Hydroxy-2-Oxo-2H-Chromen-3-Yl) Ethylidene) Benzohydrazide, a Novel Synthesized Coumarin, Ameliorates Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats through Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 6;2020:2432918. doi: 10.1155/2020/2432918. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32215169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiss N, Heydrick SJ, Postea O, Keller C, Keaney JF, Jr, Loscalzo J. Influence of hyperhomocysteinemia on the cellular redox state - impact on homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003;41:1455–1461. - PubMed
-
- Landmesser U, Spiekermann S, Dikalov S, et al. Vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic heart failure: role of xanthine-oxidase and extracellular superoxide dismutase. Circulation. 2002;106:3073–3078. - PubMed
-
- Forgione MA, Leopold JA, Loscalzo J. Roles of endothelial dysfunction in coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2000;15:409–415. - PubMed
-
- Eyries M, Collins T, Khachigian LM. Modulation of growth factor gene expression in vascular cells by oxidative stress. Endothelium. 2004;11:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Harrison D, Griendling KK, Landmesser U, Hornig B, Drexler H. Role of oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91:7A–11A. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
